Presentation
History of cosmetic breast augmentation with autologous fat injections. Came for breast evaluation before possible new lipo injections.
Patient Data

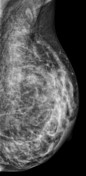
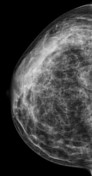
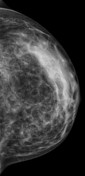
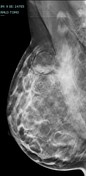

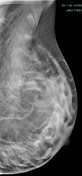

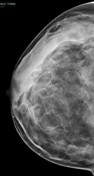

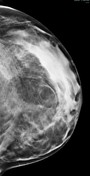

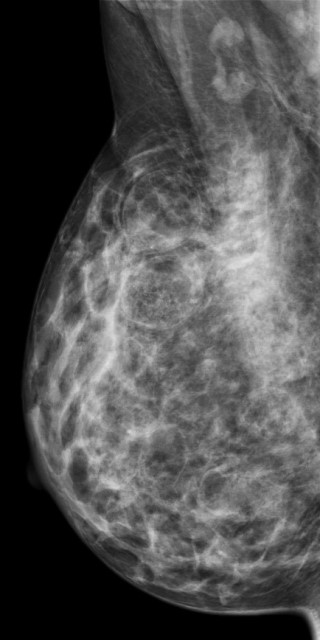
Bilateral multiple well-circumscribed variable-shaped radiolucent masses of fat density, most of them have a thin, peripheral capsule.
Few benign foci of microcalcifications are noted.
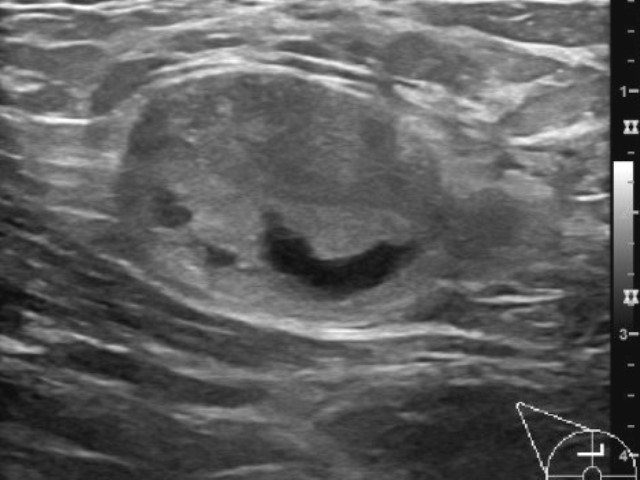
Multiple well-defined heterogenous mainly hyperechoic lesions with various shapes and sizes, some of them show cystic changes without detectable vascularity.
Case Discussion
Autologous fat injection is a widely used procedure by plastic surgeons for breast augmentation and reconstruction. The outcome varies with different techniques, one of the encountered issues is the unpredictability of breast volume maintenance as fat resorption can occur, therefore reinjection is commonly seen 1,2.
An awareness of the imaging appearances of autologous fat augmentation on mammography, ultrasound, and MRI is essential, as the findings diverge, ranging from scattered microcalcifications and simple cysts to spiculated masses 3.
Fat necrosis is a frequent complication, and the extent and stage of fat necrosis define the mammographic appearance. A radiolucent mass is observed in early fat necrosis with little or no fibrosis. More extensive fibrosis may present as a spiculated mass with calcifications 4.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.