Presentation
The patient presented with right-sided headache, vomiting and right eye pain for 2 weeks. The patient also had decreased vision in the right eye.
Patient Data
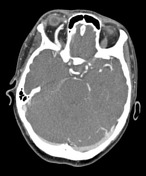

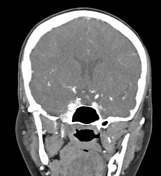

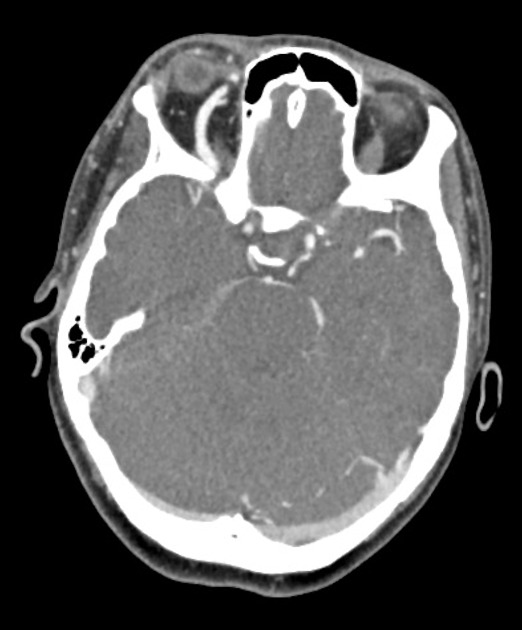
Enlarged and lobulated right cavernous sinus following arterial blood pool. Enlarged right superior ophthalmic vein with similar arterial blood pool. Retrobulbar fat-stranding with mild unilateral proptosis.
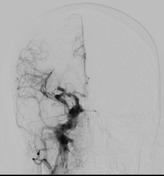



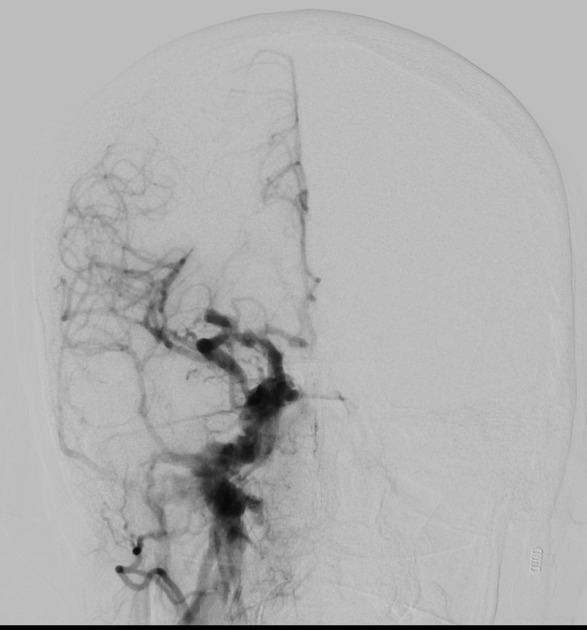
Immediate filling of the dilated right superior ophthalmic vein on the initial run via the right internal carotid artery. There is prompt filling of the cavernous sinus on coronal plane.
Case Discussion
Caroticocavernous fistulae (CCF) are abnormal arteriovenous communications between the cavernous sinus and the carotid circulation. CCF may be divided into direct and indirect classifications. The typical clinical presentation of CCF is with neuro-ophthalmic symptoms. The gold standard diagnostic modality is digital subtraction angiography (DSA).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.