Presentation
Right iliac fossa pain.
Patient Data


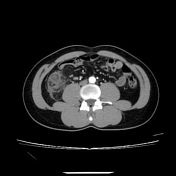

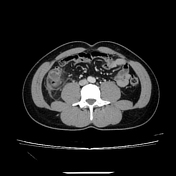

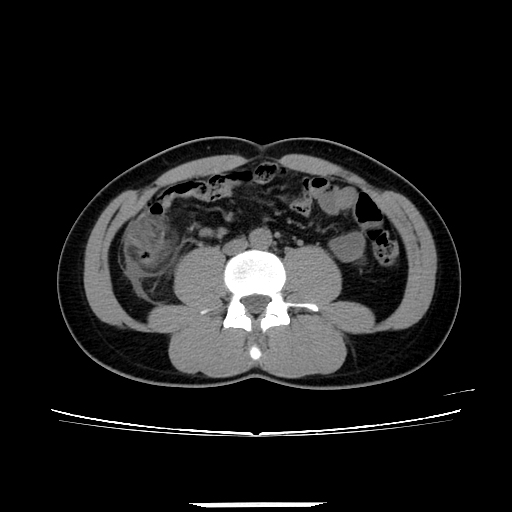
Abdominal CT imaging with contrast enhancement reveals multiple diverticula in the ascending colon and cecum. The largest diverticulum, located posterior to the ascending colon, measures approximately 11 mm, with thickened walls demonstrating strong contrast enhancement, surrounding fat stranding, and thickening of the adjacent peritoneum. The thickening of the ascending colon wall corresponds to colonic wall enhancement, characterized by inner and outer high-attenuation layers, with a thick middle layer of low attenuation.
The appendix shows no signs of inflammation.
A small amount of free fluid is present in the lower abdomen.
Case Discussion
The findings on CT imaging and clinical examination suggest ascending colon diverticulitis without complications, classified as stage Ia according to the Hinchey classification. The patient is managed with intravenous antibiotics, anti-inflammatory treatment, and rehydration.
This condition is relatively common in clinical practice, and differential diagnoses include acute appendicitis, epiploic appendagitis, omental infarction, and mesenteric panniculitis. CT imaging can assist in distinguishing these entities.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.