Presentation
Long standing rheumatoid arthritis.
Patient Data


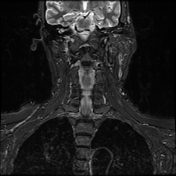

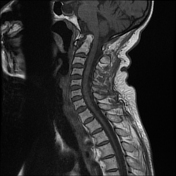

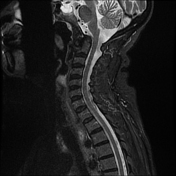

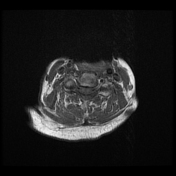



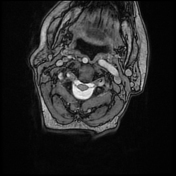

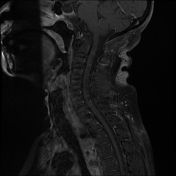

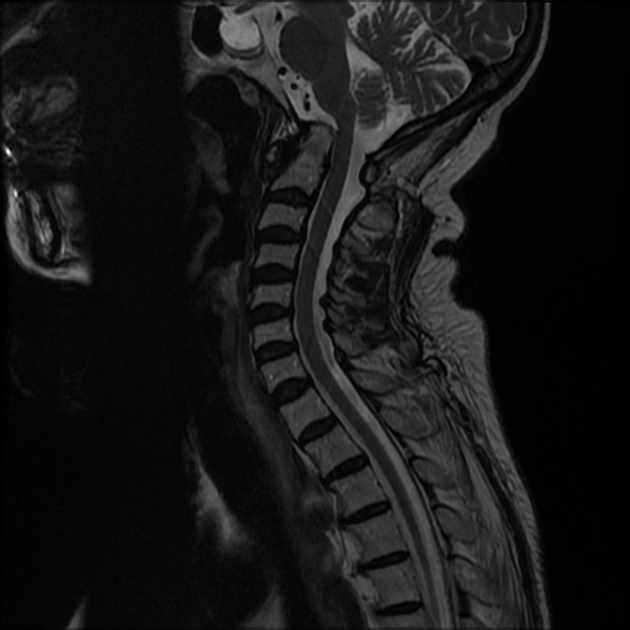
Cranial settling with anteroposterior subluxation of the atlantoaxial joint is demonstrated, as the odontoid process projects superoposteriorly, with the tip of the odontoid process at the same level as the basion. There is a widening of the atlantodental interval (~8 mm). Focal impression on the corticomedullary junction is observed due to the posteriorly displaced C2, resulting in a focal loss of the anterior arachnoid space, but without compressive myelopathy. Erosive changes are noted in the odontoid process, along with pannus formation in the atlantoaxial joint.
Case Discussion
Rheumatoid arthritis is an acquired cause of basilar invagination. Basilar invagination can manifest in isolation or with atlantoaxial subluxation or dislocation, leading to significant instability. The term "cranial settling" is used to appropriately describe basilar invagination in rheumatoid arthritis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.