Presentation
Unconscious for the past 24 hours.
Patient Data
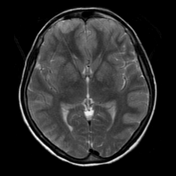

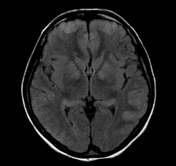

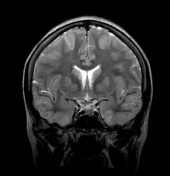

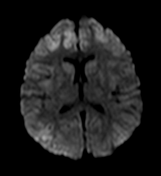

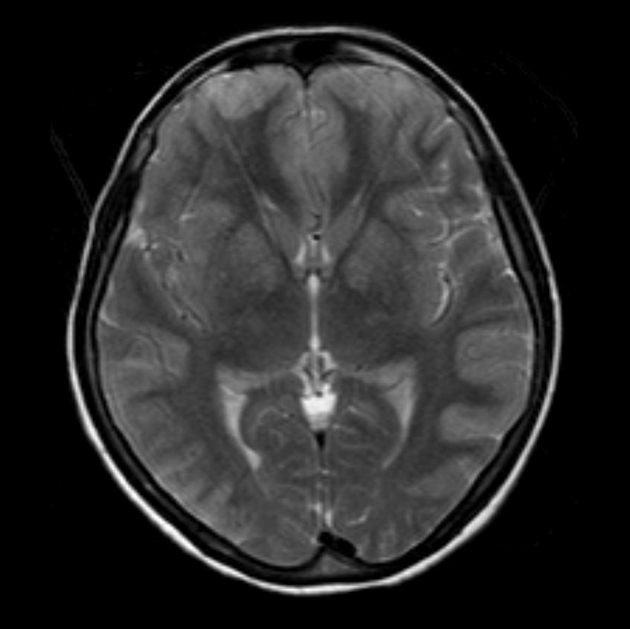
Axial T2WI and FLAIR shows symmetrical T2 prolongation in the bilateral putamina, globi pallidi and heads of the caudate nuclei.
There is also bilateral symmetrical cortical hyperintensities involving bilateral frontal, parietal and temporal lobes, including medial temporal lobes. Diffusion weighted images (DWI) and ADC maps show restricted diffusion, indicated cytotoxic edema.
Case Discussion
This individual was known to have had significant carbon monoxide poisoning the prior day.
The globus pallidus is the most common site of involvement in carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. Intense CO poisoning can also cause diffuse hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, predominantly involving the cortical grey matter.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.