Presentation
Routine ultrasound for a patient with hepatitis C led to an order of MRCP.
Patient Data

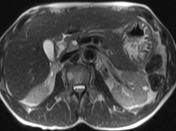
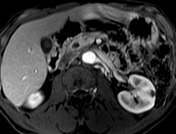
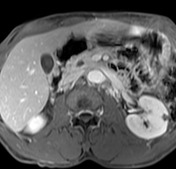
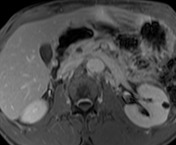
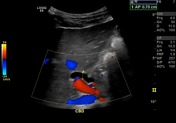
CBD dilated up to 1 cm smoothly.
No intra-hepatic dilation. No pancreatic duct dilation. No mass seen on post contrast images.
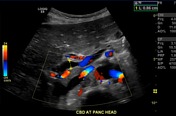

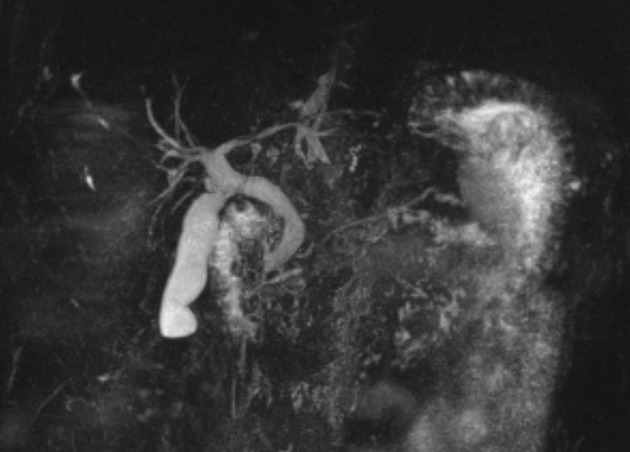
Common bile duct dilated smoothly both proximally and distally.
Case Discussion
The patient had a history of hepatitis C, but he was not a chronic alcoholic nor did he use opioids. He had no evidence of chronic pancreatitis. A routine ultrasound showed a common bile duct (CBD) dilated up to 0.8 cm. Due to the US, MRCP was ordered. There was no evidence of elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase.
Nuclear medicine biliary scan was recommended but he has not kept his follow up for this study. This would have been a non-invasive confirmatory step.
Since the patient used cocaine and there was no mass on MRI/MRCP it was felt his dilated CBD was due to cocaine-induced sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.
These days radiologists need to know non-malignant etiologies for CBD dilation.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.