Presentation
Scoliotic spine since birth. No other known congenital anomalies.
Patient Data
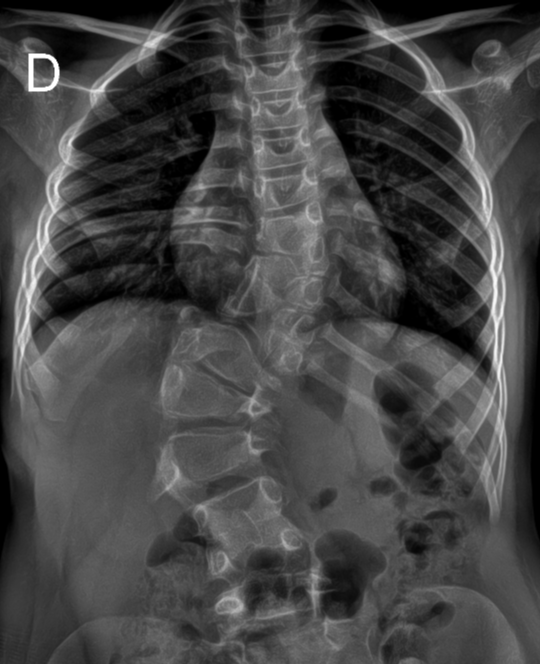
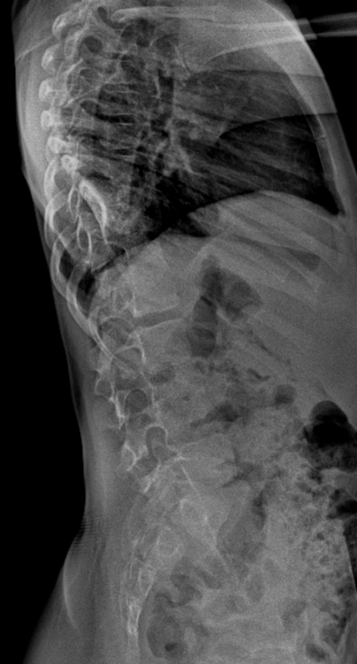

Congenital scoliosis with a right lumbar and a left thoracolumbar curves.
Multiple congenital vertebral anomalies, including:
Wedge vertebrae (hypoplastic half of a vertebral body)
Block vertebra (fused vertebrae)
Semisegmented hemivertebrae (vertebra lacking formation of half of its body and fused with the vertebra above or below)
Complex abnormality involving multiple malformed vertebrae with butterfly vertebrae (failure of fusion of the lateral halves of a vertebral body), a unilateral bar connecting the butterfly vertebrae, and two semisegmented hemivertebrae (with failure of segmentation between them)
Pelvic obliquity. Even shoulders. No coronal imbalance.
Case Discussion
Congenital osteogenic scoliosis, often called congenital scoliosis, refers to scoliosis resulting from vertebral malformations.
In this case, several types of vertebral malformations are present:
wedge vertebra: half of the vertebral body is underdeveloped
block vertebra: fusion of at least two vertebral bodies
semisegmented hemivertebra: vertebra lacking formation of half of its body and fused with the vertebra above or below
butterfly vertebra: failure of fusion of the lateral halves of a vertebral body
vertebral bar: failure of segmentation resulting in fusion of at least two pedicles
The behavior of congenital scoliosis caused by a combination of various abnormalities is extremely difficult to predict. In such cases, such as the present one, continuous follow-up is often necessary to comprehend the nature of the curve and the potential of progression.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.