Presentation
Headache and seizure.
Patient Data
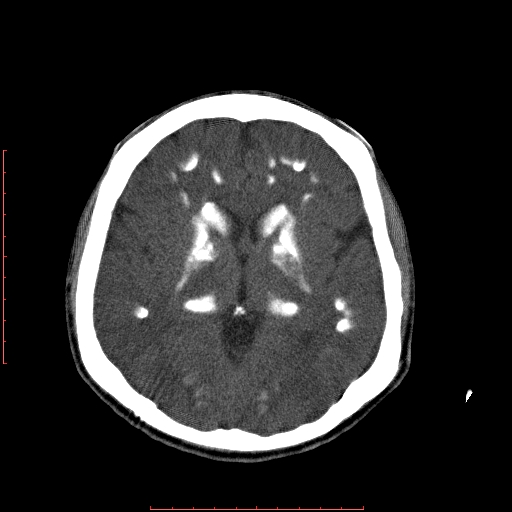
Extensive dense calcifications in the basal ganglia bilaterally, most significantly in the caudate and lentiform nuclei, as well as in the white matter supra- and infratentorially.
Case Discussion
Fahr syndrome is characterized by calcification of the basal ganglia and white matter with subsequent neuronal loss. It classified as either primary, known as primary familial brain calcification, or secondary, due to underlying metabolic, infectious and traumatic causes. The usual age of onset is between 40-50 years, and clinically the syndrome may be asymptomatic or present with a variety of neurological and psychiatric manifestations.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.