Presentation
Patient with a known history of anxio-depressive disorders presenting with seizures.
Patient Data
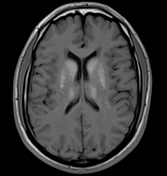

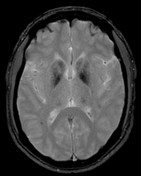

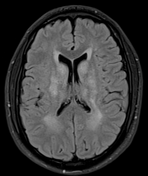

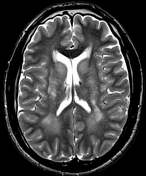

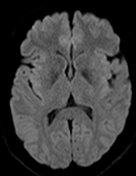

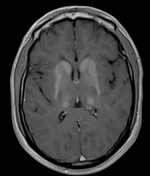

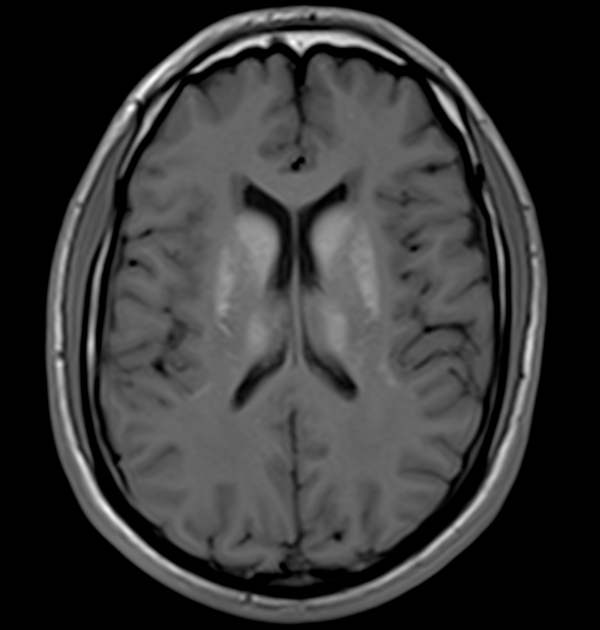
The MRI sequences demonstrate:
bilateral and symmetrical abnormal signal involvement of the caudate, lentiform nuclei, thalami and dentate nuclei as well as the deep and subcortical white matter which appear of high signal on T1 and iso to low signal on T2 with signal drop-out on GRE, in keeping with massive calcification rather than blood products
bilateral symmetrical T2/FLAIR high signal areas of the basal ganglia, the white matter of the internal capsules, corona radiata, centrum semiovale, and surrounding the dentate nuclei
no restricted diffusion on DWI/ADC or abnormal enhancement on postcontrast sequences

A complementary CT was performed confirming the calcific nature of the aforementioned lesions.
Case Discussion
Fahr syndrome, also known as bilateral striatopallidodentate calcinosis, is characterized by abnormal vascular calcium deposition, particularly in the basal ganglia, cerebellar dentate nuclei, and white matter.
It can be either primary (usually autosomal dominant) or secondary to a large number of underlying illnesses or metabolic disturbances.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.