Presentation
Dizziness, numbness and paresthesia of the limbs. Status post thyroidectomy for multinodular goiter; she is on thyroxine.
Patient Data
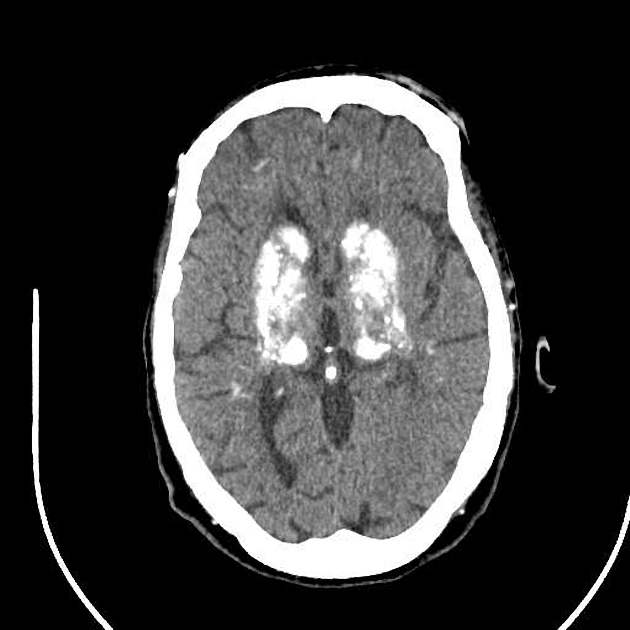
Bilateral symmetrical dense calcifications in dentate nucleus, basal ganglia, thalamus and subcortical white matter.
Case Discussion
Bilateral symmetrical dense calcifications in the dentate nuclei, basal ganglia, thalami, and subcortical white matter are pathognomonic of Fahr syndrome.
Primary familial brain calcification (Fahr disease) typically presents between 40 and 60 years of age and has a progressive course.
Calcification in a similar distribution but secondary to another disease process is referred to as Fahr syndrome. As well as thyroid disease, many other possible underlying causes have been described: see Fahr syndrome.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.