Presentation
Fever with swelling and pain in the right scrotal region. A fistulous tract extending to the skin is present. Ultrasound suggests a right testicular and epididymal abscess.
Patient Data
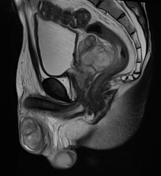

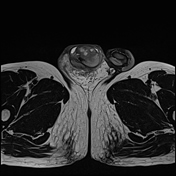

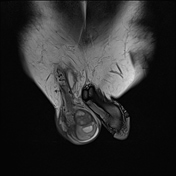

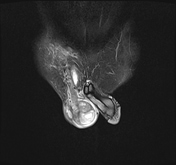

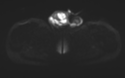

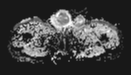

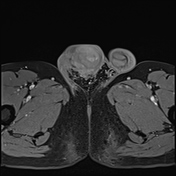

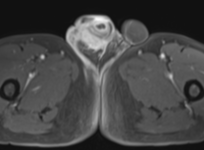

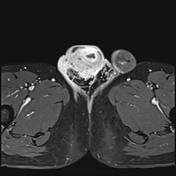

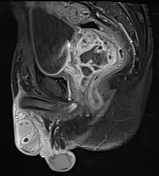

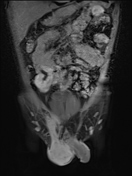

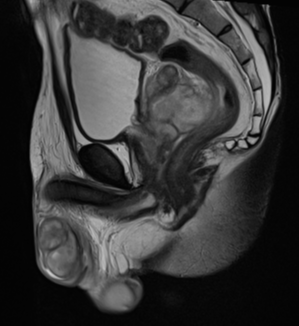
MRI demonstrates multiple fluid collections within the right testis, epididymis, and ductus deferens, associated with marked swelling, perifocal fat stranding, and extension into the scrotal skin. The inflammatory process extends along the spermatic cord and ductus deferens to the seminal vesicles and prostate in the pelvic region, forming fluid collections suggestive of abscesses (size ~51 × 41 × 44 mm) with multiple internal septations. The lesions exhibit heterogeneous hyperintensity on T2-weighted/STIR sequences, diffusion restriction, and intense, heterogeneous contrast enhancement, predominantly in the peripheral zone. A small right-sided hydrocele is also noted.
Laboratory findings:
urinary bacteria count (measured by an automated analyzer): 108,9 (significantly elevated)
blood test results show elevated white blood cell count (WBC) of 14,1 G/L and neutrophil percentage (NEU) of 86,1%
total PSA level in blood: 1,97 ng/mL (within normal range)
rapid HIV antibody test: negative
direct AFB staining with Ziehl-Neelsen in testicular pus: positive (1+)
mycobacterium tuberculosis PCR (automated system): positive (Ct: 26,76)
bacterial culture and identification (automated system) from testicular pus: negative
Case Discussion
Imaging findings and laboratory results are consistent with male genitourinary tuberculosis, involving the scrotum (testis, epididymis, and ductus deferens), seminal vesicles, and prostate.
The patient was treated with a combination of ultrasound-guided abscess aspiration and anti-tuberculosis therapy, resulting in significant improvement in both clinical symptoms and laboratory findings.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.