Presentation
Unexpected cardiac arrest with failed resuscitation. There are no known congenital cardiac abnormalities.
Patient Data


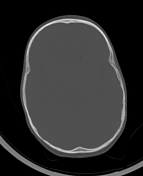

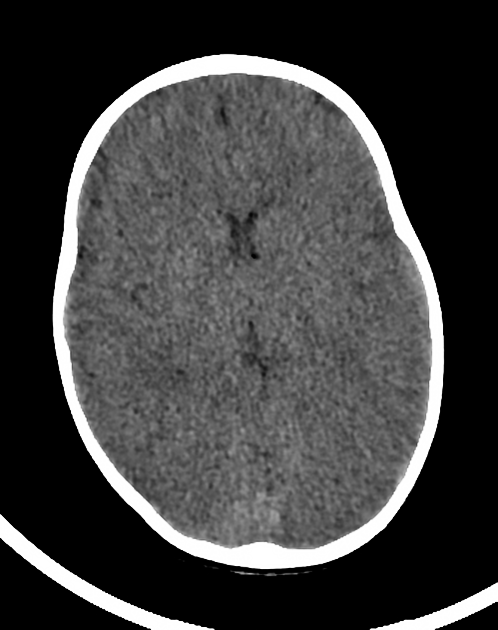
CT brain demonstrates poor grey-white matter interface with attenuated surface sulci, ventricles and cisterns with generalized cerebral edema. The dural venous sinuses appear hyperdense. There are tiny locules of intracranial and possibly intravascular gas. The cerebellar hemispheres appear mildly hyperdense.
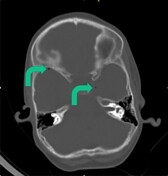
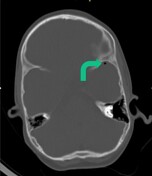
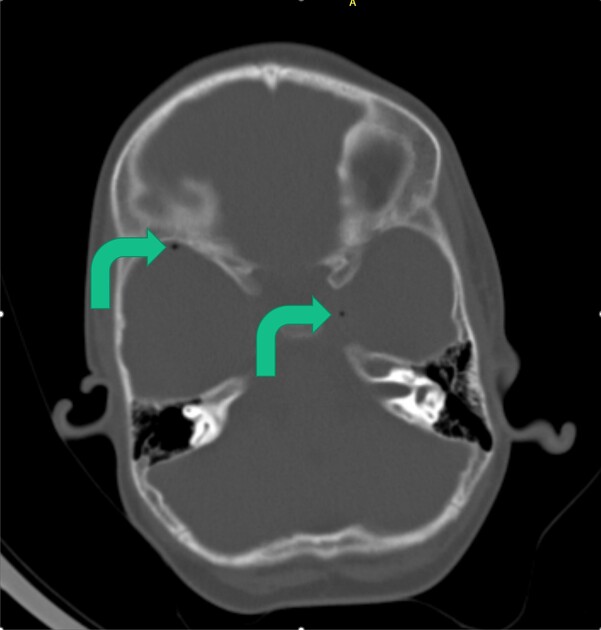
Bony windows best demonstrate the tiny gas locules. The locules are within the left cavernous sinus, bitemporal and possibly within the vertebral artery.
Case Discussion
A case of global hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy with a performance of the CT brain within 4 hours of the patient's demise.
There is a white cerebellum sign also known as the dense cerebellum or reversal sign appreciated as such due to the low-density supratentorial cerebral hemispheres secondary to anoxic ischemic brain injury. The dural venous sinuses are also dense.
Intracranial/intravascular gas locules also suggest brain death and may represent extremely early putrefaction. These gas locules are best appreciated on the bony windows and may easily be missed on the normal brain windows as in this instance.
It is important to note that brain death cannot be established on CT of the brain and requires a combination of clinical, biochemical and perfusion investigations. These differ from country to country.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.