Presentation
History of gastric content emesis and decreased oral tolerance of 10 days.
Patient Data
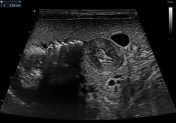
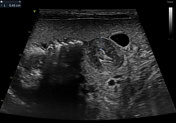
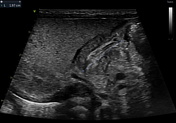
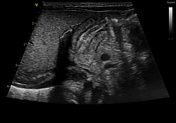
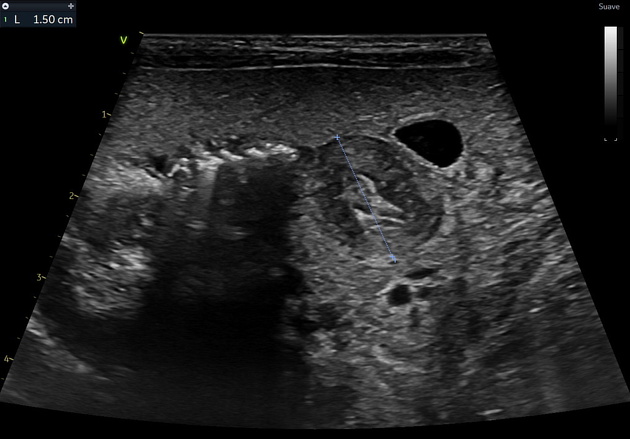
Ultrasonography reveals a dilated gastric chamber with a 4.5 mm thickened pylorus wall, measuring 15 mm transversely and 19.7 mm longitudinally, indicating hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
Case Discussion
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis consists of a pyloric canal narrowing due to hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter muscular layer, causing a partial obstruction of the gastric outlet. This pathology is more common in male patients between 6 weeks and 3 months old. It presents as non-bilious vomits more commonly after feeding, which can cause dehydration, weight loss, and malnutrition in severe cases.
Ultrasound is the most appropriate imaging technique for diagnosing, as in this case, where it reveals a pyloric muscle thickening and an enlarged length and transverse diameter, as previously mentioned. The patient was taken to surgery, and a pyloromyotomy was performed.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.