Presentation
Antibiotically treated PROM. Neonate developed a subfebrile fever, CRP on the rise - abdominal US ordered.
Patient Data
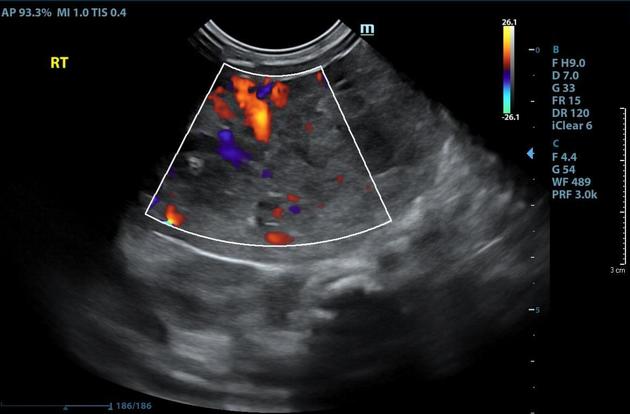
Solid exophytic mass bulging from the right hepatic lobe, measuring 6 cm in its longest axis, with a heterogeneous echotexture and internal flow.
The liver itself is of normal size and texture. The gallbladder is contracted.
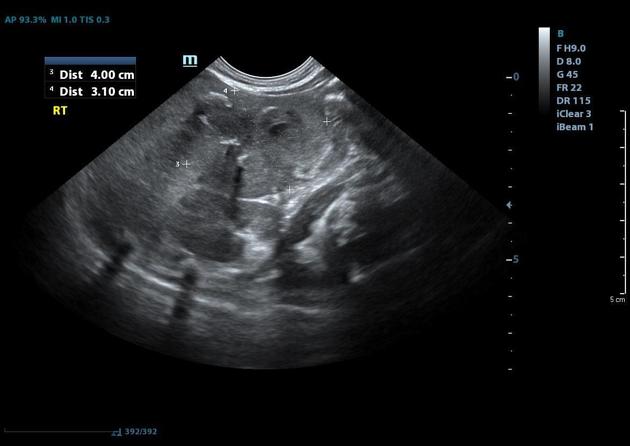
Known exophytic hepatic hemangioma now measuring 4.5 cm in its longest axis, with several internal foci of coarse calcification.
Case Discussion
Term neonate, vaginal delivery, APGAR 9/10. At the age of 1 day developed a fever of 37.7°C. WBC 21.8K x 109/L, blood culture positive for gram-variable cocci, later identified as Micrococcus luteus. Treated with ampicillin and gentamycin for 2 days, as repeat blood and cultures were sterile, and a stool sample and nasal swab yielded no pathogens. The baby herself was well. Nonetheless, the WBC count remained high and CRP continued to rise. Treatment with Tazocin (piperacillin/tazobactam) was initiated and an abdominal ultrasound was ordered. CRP rose to a maximum of 111 so amikacin was added.
Abdominal US was normal except for an incidentally discovered exophytic vascular hepatic mass. CT abdomen (not available) showed it to be a large hemangioma in the 7th segment not in contact with any large portal vessel or artery and draining into the right hepatic vein. Treatment with propranolol 1 for the hemangioma was initiated and the infant was discharged.
Repeat US one month after the first one showed that the hemangioma had shrunk and that calcifications had formed within it, as expected for a treated hemangioma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.