Presentation
Pain in right groin without any history of trauma or positive clinical findings of infection.
Patient Data

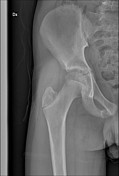
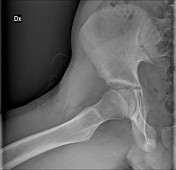
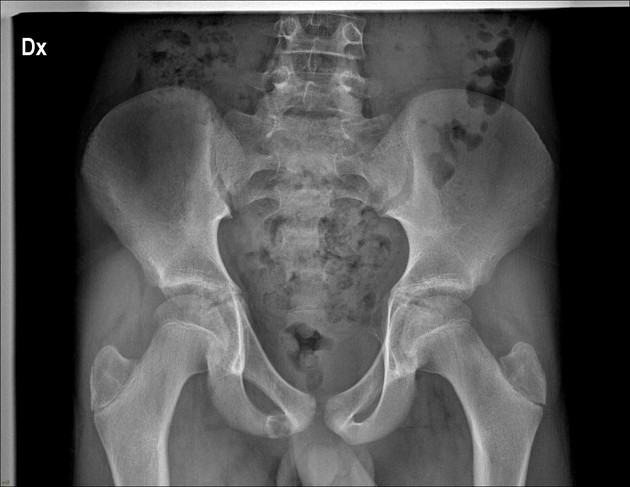
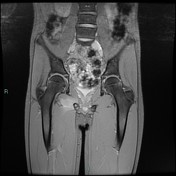
Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph shows enlargement of the right ischiopubic synchondrosis with radiolucency.
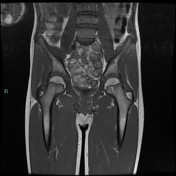

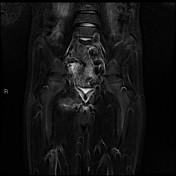


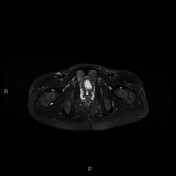

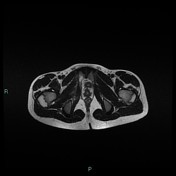

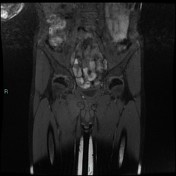

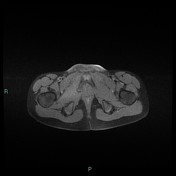

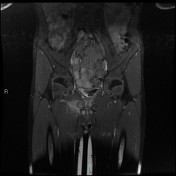

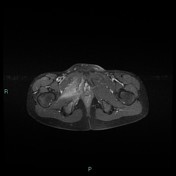

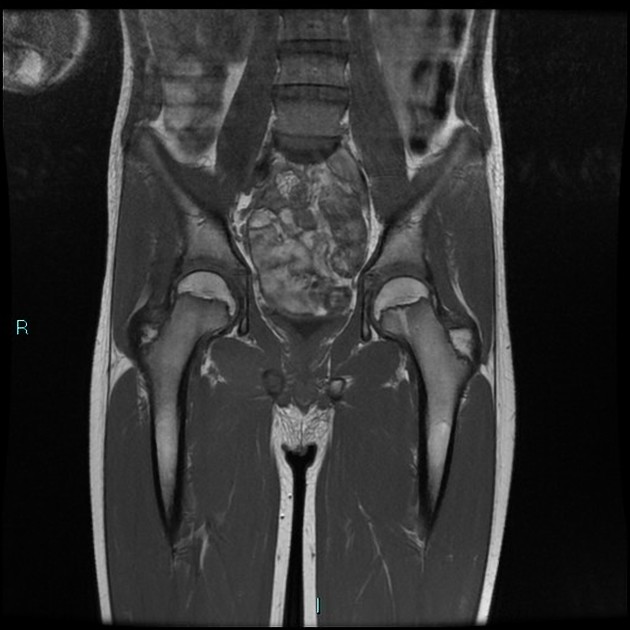
T2 magnetic resonance image demonstrating right ischiopubic syncondrosis enlargement with irregular edges and bone marrow edema; edema of the external obturator muscles and large adductor is associated.
Case Discussion
Van Neck-Odelberg disease is a syndrome characterized by an atypical ossification pattern of the ischiopubic synchondrosis. Its radiological features may mimic stress fracture, neoplasm, osteomyelitis, or posttraumatic osteolysis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.