Klebsiella pneumoniae necrotizing fasciitis - post intramuscular injection
Presentation
Right gluteal swelling, pain and fever developed following right gluteal analgesic injection.
Patient Data
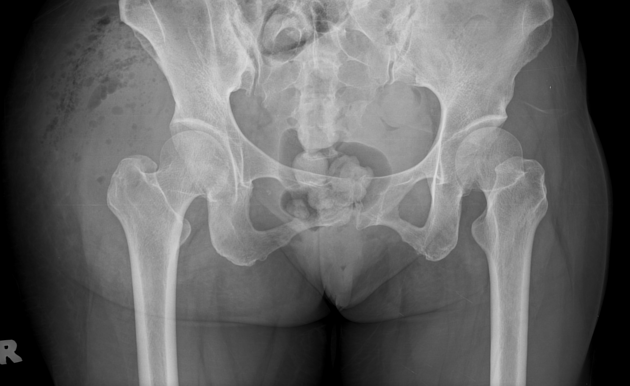
Abnormal right gluteal soft tissue swelling associated with multiple streaks of gas lucency, suspicious for necrotizing fasciitis and abscess due to gas-forming organisms.
No abnormal lytic or sclerotic bony lesions. No abnormal periosteal reaction.
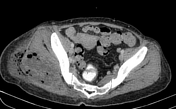

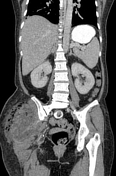

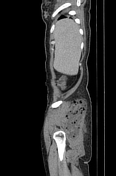


Large peripherally enhancing multi-loculated low-attenuating collection in liver segments 2 and 3. Long segment filling defect seen in the draining left hepatic vein extending into the suprahepatic portion of the inferior vena cava in keeping with thrombophlebitis. No extension into the right atrium.
Multiple scattered small hypodense lesions throughout the enlarged liver (20.5cm).
No ascites. No abdominal or pelvic lymphadenopathy.
The spleen is enlarged (13.0cm) without any focal lesion or collection.
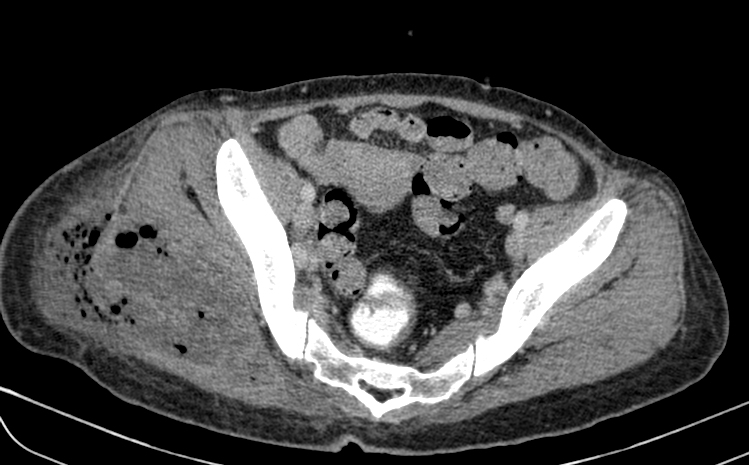
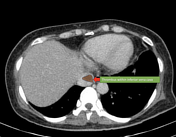
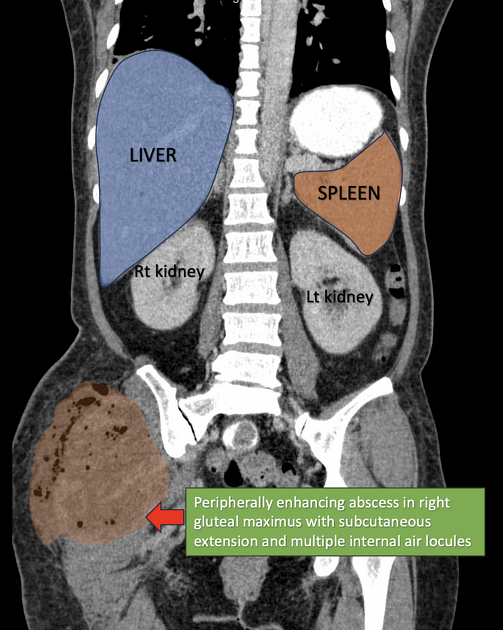
Spreading peripherally-enhancing multi-loculated fluid and gas collections in the right gluteal region involving the right gluteal maximus muscle and adjacent soft tissues. Part of the collection extends into the subcutaneous tissue with surrounding fat stranding. No extension into the right hip joint. The adjacent right pelvic bone and right femur are intact without osteomyelitic changes.
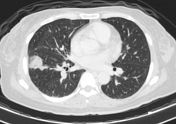
Focal areas of ground glass opacity in the posterobasal segment of left lower lobe and laterobasal segment of right lower lobe. Cavitating lesion in the right lower lobe. Multiple tiny lung nodules in the lung bases.
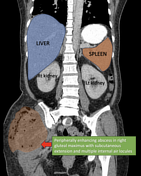
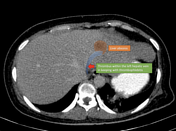
Annotated images showing the right gluteal necrotizing fasciitis and the left hepatic vein thrombophlebitis extending into inferior vena cava.
Case Discussion
The right gluteus maximus pyomyositis is complicated by abscess formation with peripheral enhancement and spreading necrotizing fascitis in the adjacent soft-tissues.
The gluteal abscesses were drained surgically and the left liver abscess was drained percutaneously. The abscesses and blood cultures all grew Klebsiella pneumoniae.
The patient had hyperglycemia and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. This is a known risk factor for disseminated Klebsiella infection. This patient is from South East Asia where specific types of severe community-acquired K. pneumoniae infections are prevalent and these are commonly complicated by septicemia and liver abscess 1.
Septic thrombophlebitis is an important complication leading to septic pulmonary emboli in this case.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.