Presentation
Right loin pain. Suspected renal/ureteric stone. Incidental finding on CT-UT.
Patient Data
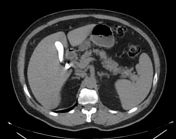

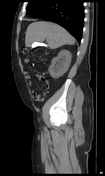

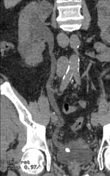

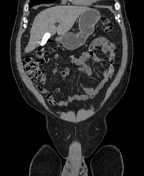

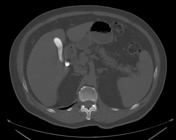

Right distal ureteric stone (within the right distal vesicoureteric junction) is seen, associated with proximal moderate hydroureteronephrosis.
Multiple right simple renal cortical cysts and left simple renal cortical cyst.
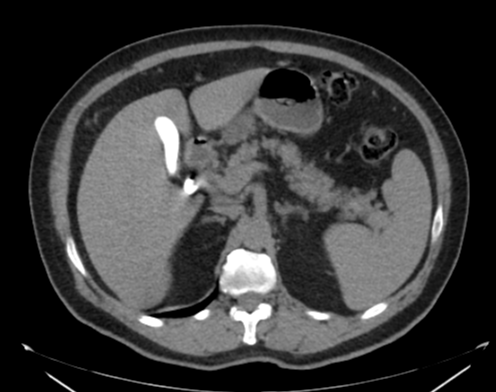
The gallbladder shows a stone impacted within its neck, another stone is seen within its fundus. The gallbladder is distended by markedly radio-opaque material.
Left gluteal intramuscular lipoma shows internal small rounded calcific granulomas, likely sequela of prior IM injection.
Case Discussion
Limy bile or calcium milk gallbladder is caused by presence of a viscous substance in the gallbladder and/or bile ducts, probably as a result of stasis. In most of the cases, the gallbladder had been obstructed by an impacted stone in its neck or cystic duct (as in this case). The patient denied any history of recent contrast uptake or intervention.
Limy bile may be an incidental finding on x-ray or unenhanced abdominal scans performed for other reasons. It appears distended by densely radio-opaque material.
DDx includes opacification by contrast material following oral cholecystography or ERCP, vicarious excretion due to renal or hepatic failure, gallbladder sludge, gallbladder stones and porcelain gallbladder.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.