Presentation
Recurrent right lower abdominal pain.
Patient Data
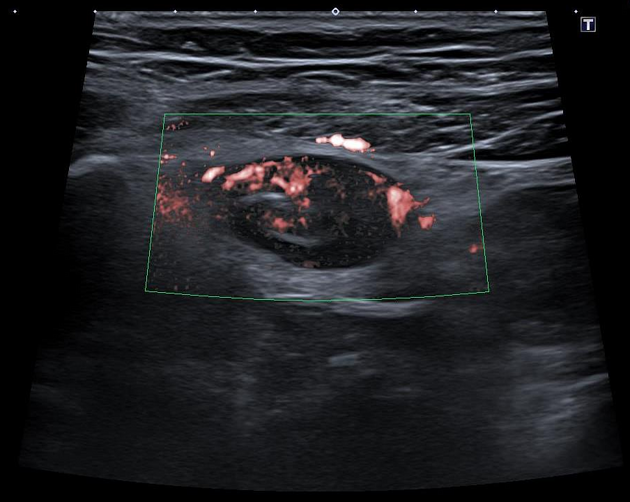
Distended and incompressible blind-ending hypoechoic tubular structure in the right flank with prominent surrounding echogenic fat and increased vascularity on superb microvascular imaging (SMI).
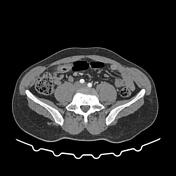

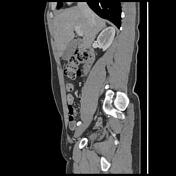

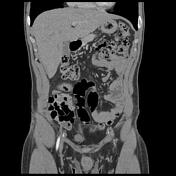



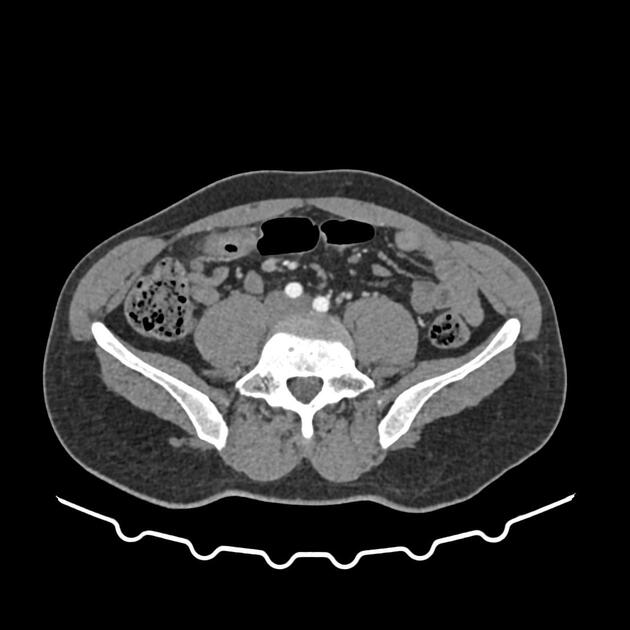
Blind-ending tubular structure with thick enhanced wall communicating with small bowel with a wall-to-wall and surrounding inflammatory changes. No evidence of perforation or hemoperitoneum. No intraperitoneal free fluid.
The appendix is of retrocecal location with a normal appearance. Normal appearance of the terminal ileum well-demonstrated on zoomed images.
Case Discussion
The ultrasound and CT features of an inflamed tubular structure with normal appearance of the terminal ileum and appendix, most consistent with a Meckel diverticulitis.
Meckel diverticulitis is the inflammation of a Meckel diverticulum, which is the most common congenital structural abnormality of the gastrointestinal tract. It is considered an uncommon cause of acute abdomen and is often not correctly diagnosed pre-operatively.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.