Patient Data
- Note: This case has been tagged as "legacy" as it no longer meets image preparation and/or other case publication guidelines.
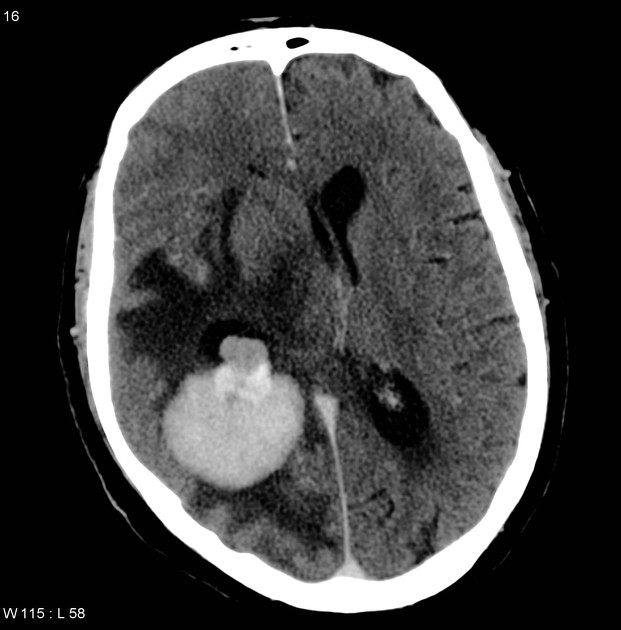
There is a large, vividly and homogeneously mass lesion, part of it appears intraventricular within the trigone of right lateral ventricular and a large part in the adjacent right parietal lobe. The mass is well defined, associated with a significant positive mass effect in the form of mid-line shift into the left side, dilatation of the left lateral ventricle and entrapment of the ipsilateral right-sided temporal horn.
Surrounding the mass, is a large area of white matter hypodensity in the right frontal, parietal and temporal lobes, most in keeping with vasogenic edema.
Conclusion:
Imaging differential diagnosis includes an intraventricular meningioma with brain parenchymal extension. and (less likely) primary CNS lymphoma.
Case Discussion
The patient went on to have a resection.
Histology
Sections show a meningioma comprised of cells with elongated to round nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm with ill-defined cell boundaries. There is extensive collagen deposition within the tumor. Most of the tumor nuclei are rather large and show prominent nucleoli. Mitotic figures are seen within the tumor and in most areas number approximately 1-3 per 10 high-power fields
At least one area, however, shows 6 mitotic figures per 10 high-power fields. Additionally, there are a few areas of microscopic necrosis, and in some areas, the nuclei are quite crowded.
At the periphery of the tumor, fragments of brain are evident. In these fragments of brain there are clusters of cells with rounded nuclei and anuclear zones. Microcystic areas are also evident in these regions.
Immunohistochemistry shows the meningioma is positive for vimentin and focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen, and negative for keratin. There is intense positivity in the brain for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)and some process positivity for vimentin and keratin. The meningioma shows scattered MIB1-positive nuclei, whereas the brain tissue shows only occasional positive nuclei.
Final Diagnosis: Atypical meningioma, predominantly fibroblastic, with brain invasion.
Comment:
In view of the brain invasion, mitotic figures, areas of necrosis, hypercellularity, and prominent nucleoli, this intraventricular tumor is designated as an "atypical" meningioma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.