Presentation
Admitted with sudden onset of right lower-middle quadrant pain and tenderness to the emergency unit.
Patient Data
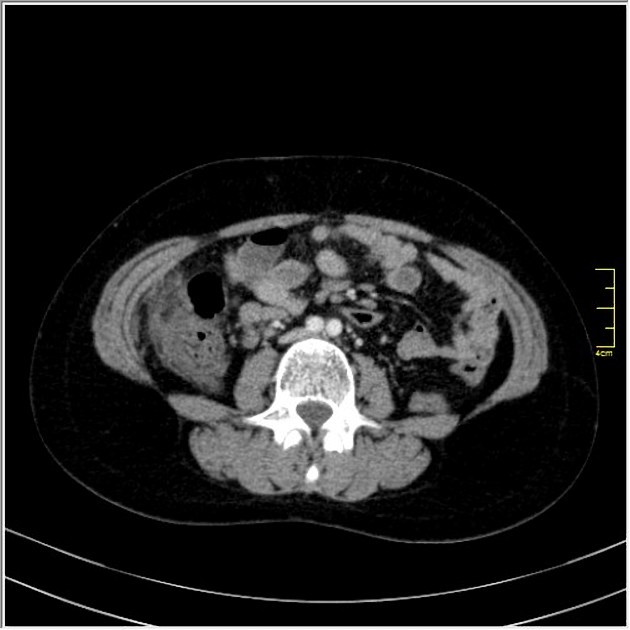
Contrast-enhanced CT shows a round shaped infiltration of the omental fat tissue with colonic wall thickening located to the anterior of the cecum and ascending colon. The diagnosis of omental infarction was confirmed by surgery.
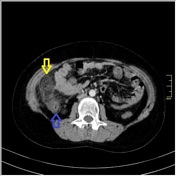
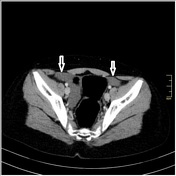
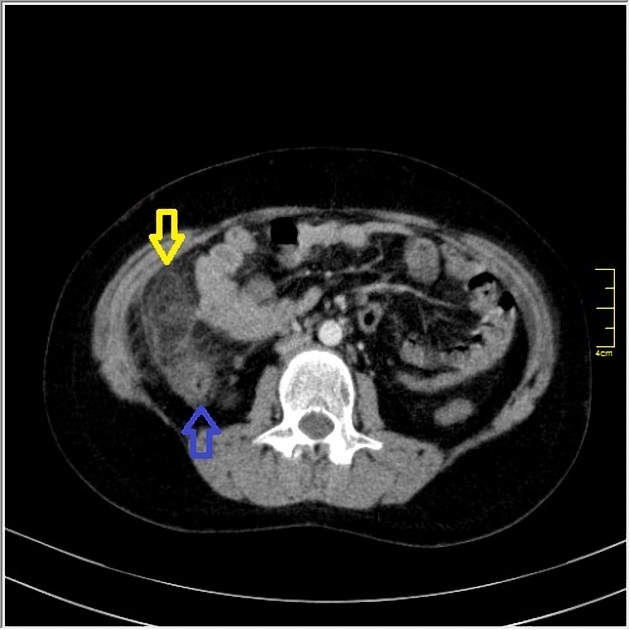
Axial contrast-enhanced CT shows a round shaped infiltration of the omental fat tissue (yellow arrow) with colonic wall thickening (blue arrow) which is located to the anterior of cecum and ascending colon. There is minimal-moderate free fluid in pelvic region (white arrows)
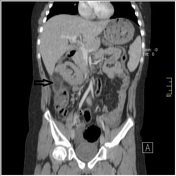
Coronal contrast-enhanced CT shows a round shaped infiltration of the omental fat tissue (black arrow)
Case Discussion
Primary omental infarction is usually seen in the right lower quadrant. This condition is often self-limiting and can be managed conservatively but sometimes require surgery because of complications or persistance of pain.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.