Presentation
Facial trauma and right eye movement limitation and preseptal swelling.
Patient Data
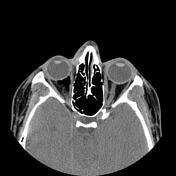

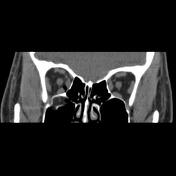

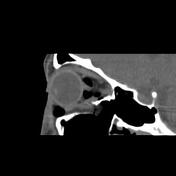

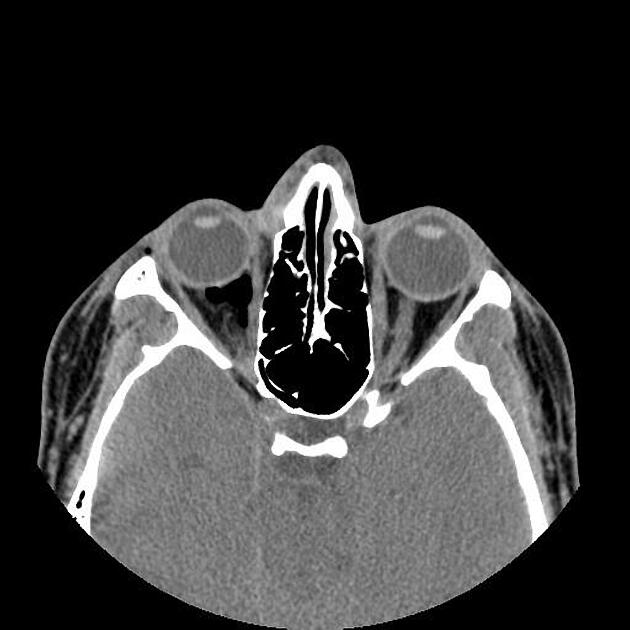
There are displaced comminuted fractures in the right orbit floor with orbital fat and inferior rectus muscle herniation within the fracture defect, remarkable postseptal intraconal more in nasal side emphysema and right lower lid subdermal emphysema. The orbital apex and optic canal are unremarkable and the fracture occurred medially to the infraorbital canal. Note also the right nasal wall displaced fracture.
Case Discussion
The case is a 25-year-old male with a history of facial trauma who came to the emergency room with right side lower eyelid remarkable swelling and right eye movement limitation. The orbital MDCT requested and entrapped orbital fat and inferior rectus muscle within the right orbit floor blow-out fracture and lower lid and postseptal intraconal orbital cavity emphysema were found. The orbital MDCT is the imaging modality of choice for blow-out fracture diagnosis and evaluation for complications such as inferior rectus muscle entrapment.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.