Presentation
Headache and intractable vomiting.
Patient Data
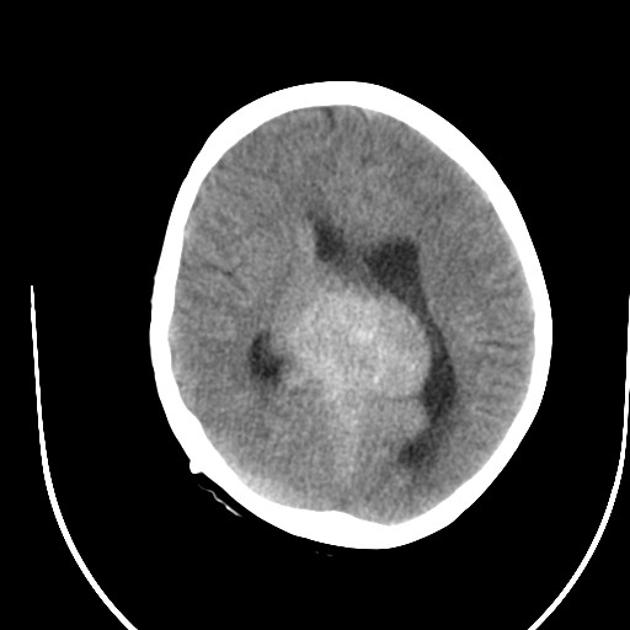
Axial brain CT images show a large hyperdense lobulated mass in the pineal region with peripheral foci of calcification and associated hydrocephalus. A VP shunt has recently been inserted (note the small amount of pneumocephalus). Hyperdense material is seen coating the frontal horns of the lateral ventricle and filling the floor of the third ventricle.
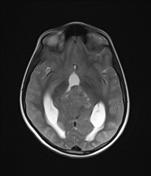

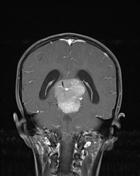

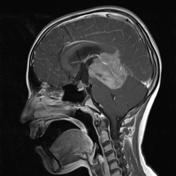

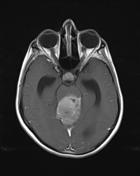

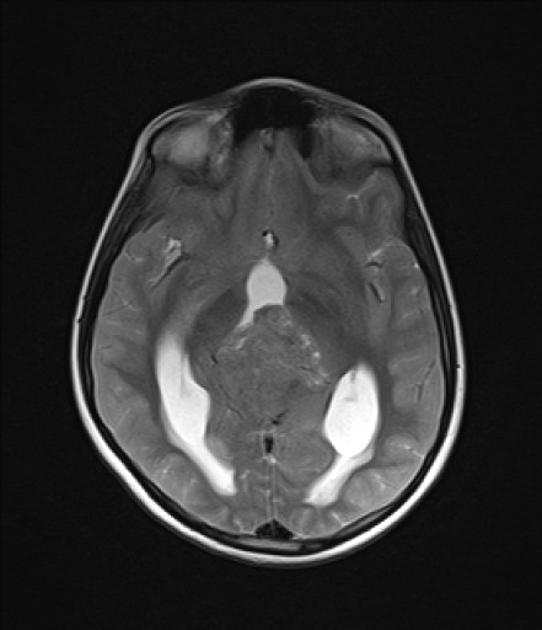
MRI obtained a number of weeks earlier (before the VP shunt was inserted) demonstrates a large pineal region mass with intermediate signal intensity on T2W images. Hydrocephalus and periventricular CSF flow (interestitial edema) are also visible.
Post contrast T1W images shows mildly heterogenous but vivid enhancement with invasion to the quadrigeminal plate, third ventricle and superior cerebellum.
Two regions of ependymal enhancement are seen in frontal horns of lateral ventricles as well as filling of the infundibular and supraoptic recesses of the third ventricles. Leptomeningeal enhancement is also prominent elsewhere. These are in keeping with ependymal dissemination.
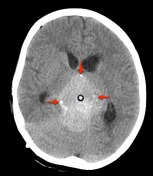
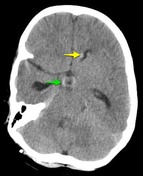
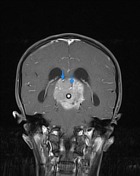
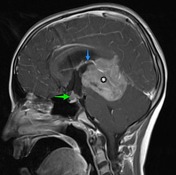
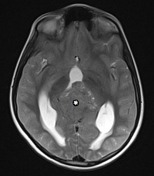
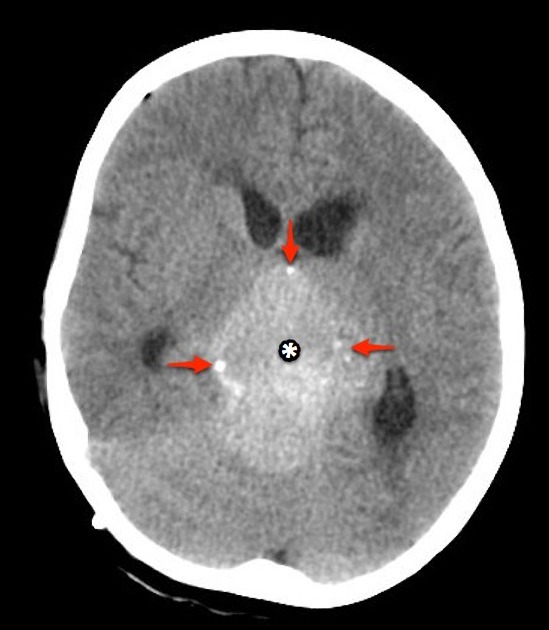
A large mass ( * ) centered on the pineal region elvates, splays and partially engulfs the internal cerebral veins (blue arrows). Pineal calcifications (red arrows) are best seen on CT and are located at the periphery of the mass.
Enhancing soft tissue is also seen filling the floor of the third ventricle (green arrows) and in the lateral ventricles (best seen in the left forntal horn - yellow arrow).
Case Discussion
This patient went on to have a biopsy which confirmed the diagnosis of a pineoblastoma.
Pineoblastoma and germinoma are two main differential consideratins in the pediatric pineal region tumors.
These tumors are both hypercellular lesions that share some imaging charachteristics (intermediate signal on T1 and T2 weighted images, CT hyperdensity and vivid contrast enhancement) as well as having a predilection of CSF dissemination. Germ cell tumors like germinoma engulf pineal gland calcification whereas pineoblastoma tend to disperse normal pineal calcification; thus the calcifications in these tumors are located peripherally.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.