Presentation
Trauma with displaced pelvic fractures.
Patient Data
This case featured in our 2016 Trauma Radiology Course which is now available to view online.
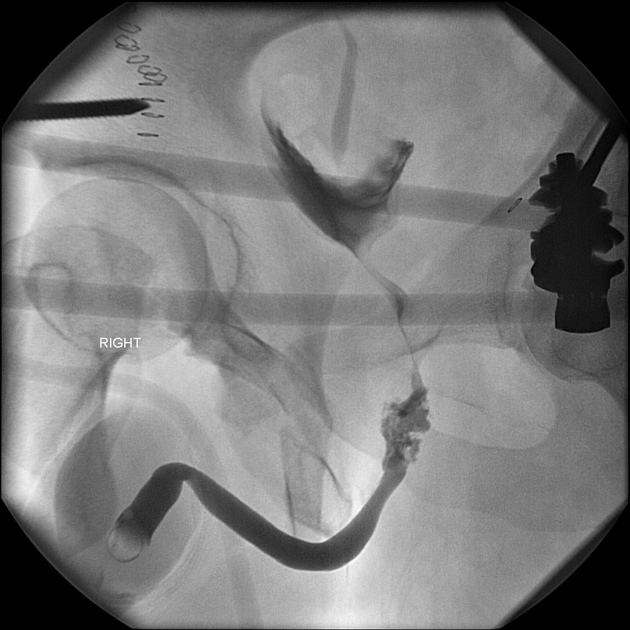
Retrograde urethrogram in a patient with pelvic fractures demonstrates contained contrast leakage at the posterior urethra (membranous portion). Contrast does ascend into the bladder and therefore the urethral injury is incomplete. Contrast in the right ureter was due to previous renal excreted contrast from a CT study rather than reflux.
Case Discussion
Typical location and appearance of a traumatic urethral injury involving the posterior urethra. This site is susceptible to injury as the puboprostatic ligaments are firmly attached to the base of the prostate at this location and produce a strong shearing force if the pubic bones or pubic symphysis become displaced.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.