Unilateral pulmonary edema: Blalock-Taussig shunt in pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect
Patient Data

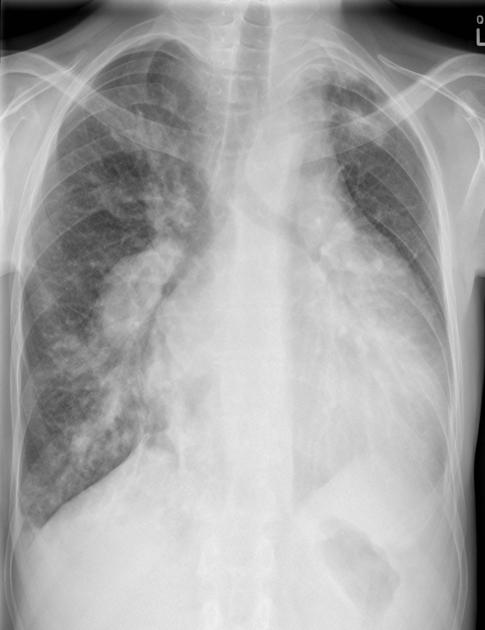
Posteroanterior chest radiograph demonstrate marked cardiomegaly with plethoric right lung. The right pulmonary artery are marked dilated receiving arterial blood from the BT shunt. The BT shunt (systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt) presents a volume load to the heart and sequelae of congested cardiac failure is evident.
Case Discussion
The patient had cyanotic congenital heart disease with underdeveloped subpulmonic infundibulum/pulmonary valve atresia and associated ventricular septal defect (VSD). The patient underwent modified Blalock-Taussig (BT) shunt procedure and VSD repair in infancy. The modified BT shunt procedure entails the use of a synthetic graft, usually polytetrafluoroethylene, with anastamotic connection between the right subclacian artery and the right pulmonary artery.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.