Birth trauma (a.k.a. birth injury) relates to those conditions caused by both physical/mechanical and hypoxic injuries.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Birth trauma occurs in ~5 per 1000 births 2.
Risk factors
- asphyxia
- breech presentation
- shoulder dystocia
- instrument delivery
- macrosomia
- obstructed labor
Pathology
Etiology
There are a wide range of conditions related to birth trauma, ranging from superficial and minor injuries through to fatal injuries.
Musculoskeletal
- superficial bruising, grazes and lacerations
- caput succedaneum
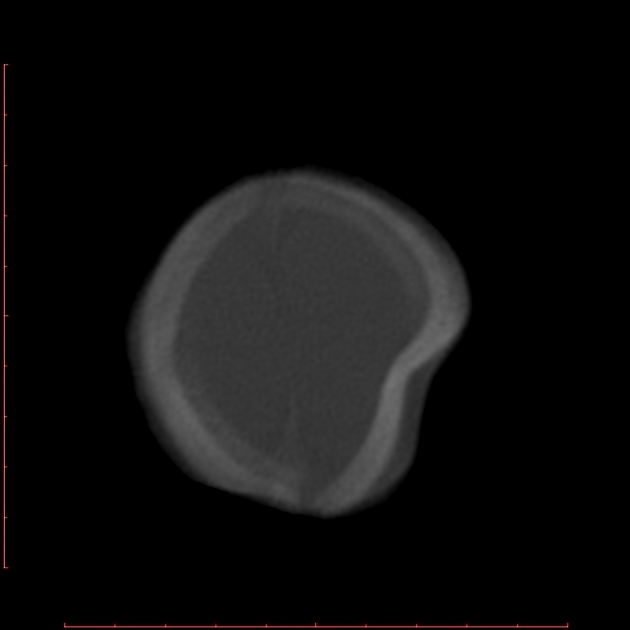
- cephalohematoma
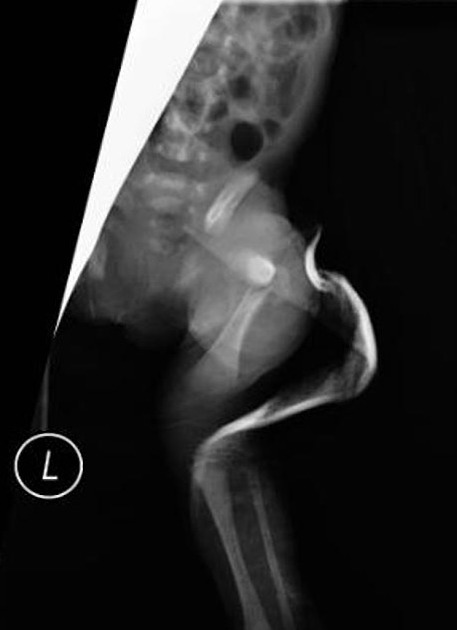
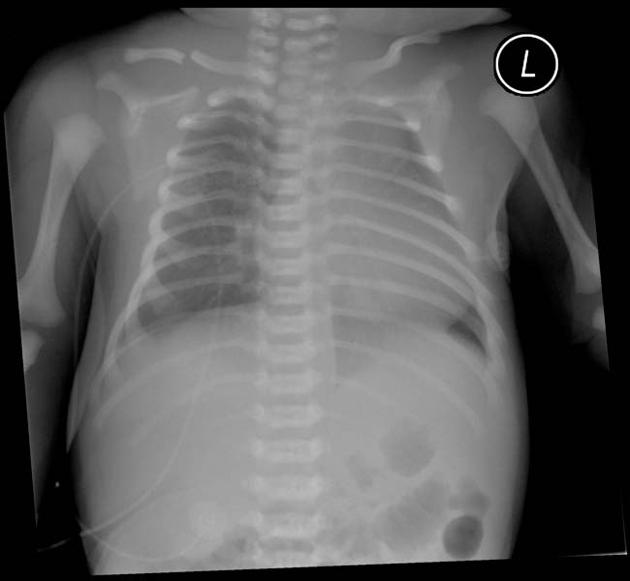
- long bone fractures, especially clavicular and femoral
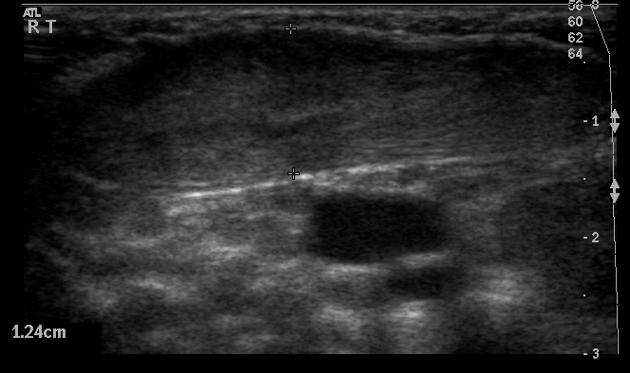
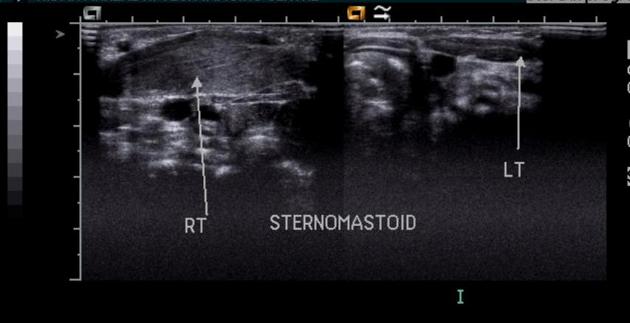
- fibromatosis colli
- skull fracture
- vertebral fractures, in particular of C7 and T1 2
CNS/PNS
- brachial plexus injury
- congenital facial nerve palsy
-
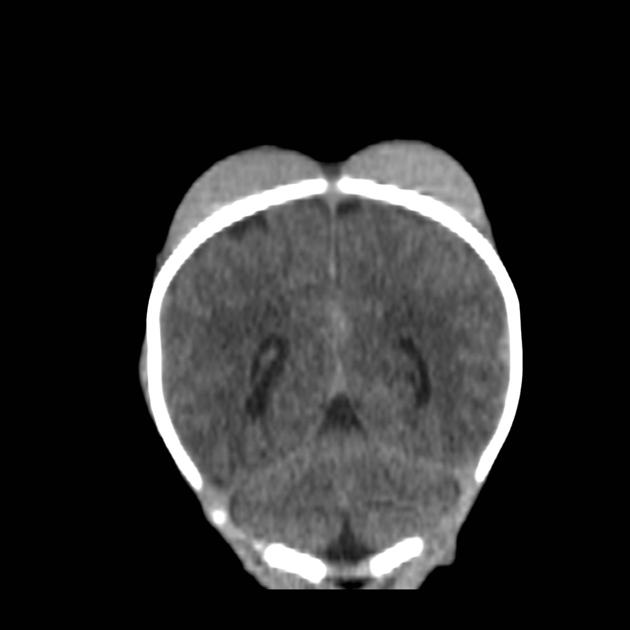
intracranial hemorrhage (ICH)
- subdural hemorrhage (most common ICH)
- extradural hemorrhage (rare)
- neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- spinal cord injury
Differential diagnosis
Birth trauma may not be readily apparent initially, and may have a delayed presentation. Non-accidental injuries can be considered in the neonate in the correct context.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.