Ciliary ganglion
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
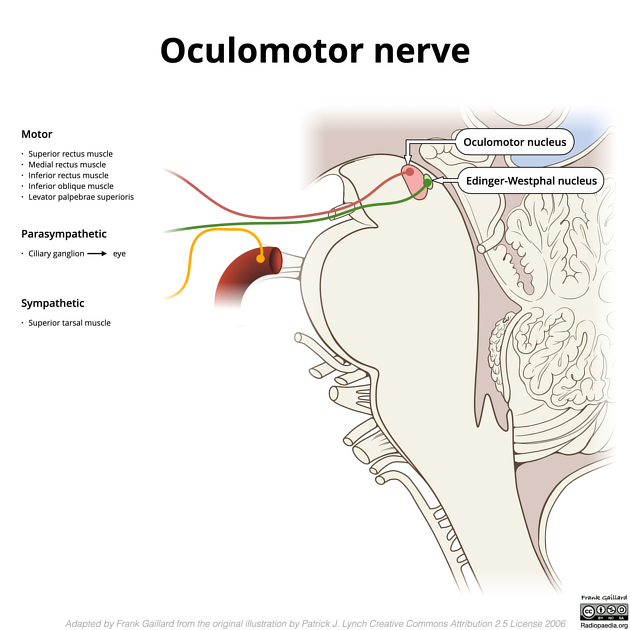
The ciliary ganglion is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. It receives parasympathetic fibres from the oculomotor nerve.
Gross anatomy
- smallest of the ganglia (2mm in size)
- located posterolaterally in the intraconal space of the orbit (towards the orbital apex) between the optic nerve and the lateral rectus muscle
- just lateral to the ophthalmic artery as it crosses the optic nerve from lateral to medial
Roots
- parasympathetic root (fibres synapse in the ganglion)
- from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus of the oculomotor nerve
- sympathetic root (fibres pass through the ganglion without synapsing)
- from the ICA (from the superior cervical ganglion) via the nasociliary nerve
- sensory root (fibres pass through the ganglion without synapsing)
Branches
- short ciliary nerves from the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve which supply the ciliary body (for accommodation) and the sphincter papillae (for pupillary constriction)
Related pathology
-
Pathologypathology of the ciliary ganglion can produce a tonic pupil, where the pupil does not react to light and slowly accommodates - Adie syndrome: when a non-reactive, slowly accomodating pupil is associated with absent deep tendon reflexes and diaphoresis






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.