Coracoclavicular ligament
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Wong A, Hacking C, Jabaz D, et al. Coracoclavicular ligament. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 04 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-33443
Permalink:
rID:
33443
Article created:
13 Jan 2015,
Aaron Wong
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Aaron Wong had no recorded disclosures.
View Aaron Wong's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures
Revisions:
13 times, by
8 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Coracoclavicular ligaments
- CC ligament
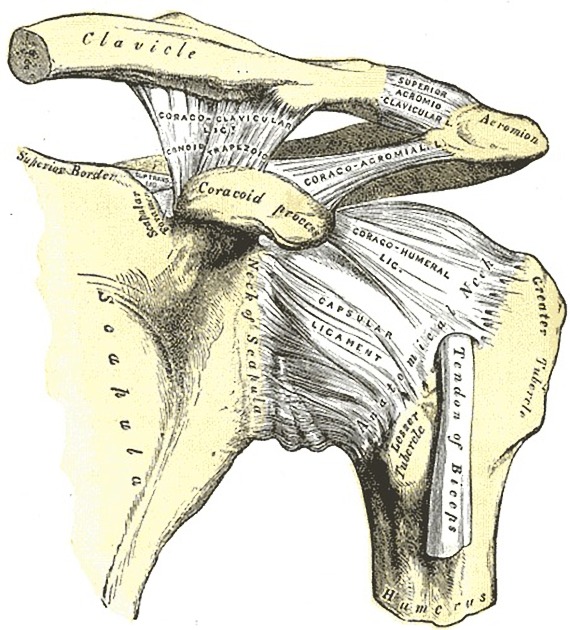
The coracoclavicular (CC) ligament is the major vertical stabilizing factor of the acromioclavicular joint.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
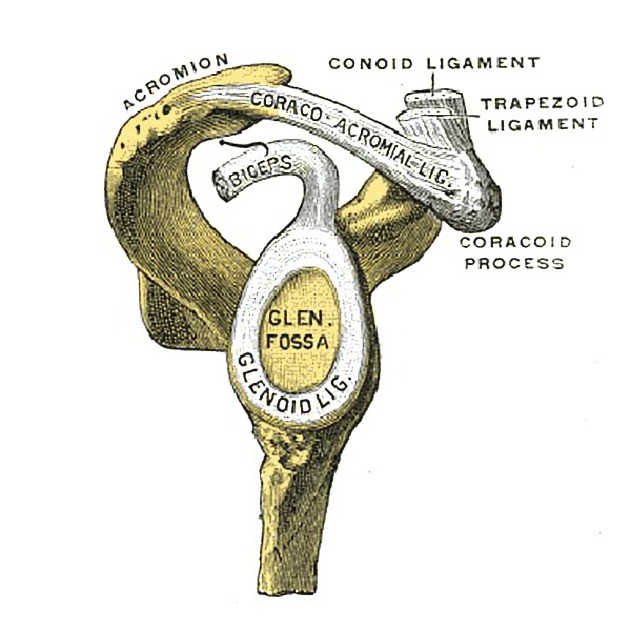
The coracoclavicular ligament can be divided into two parts: the more medial conoid ligament and the more lateral trapezoid ligament.
-
conoid ligament
- origin: knuckle of the coracoid process of the scapula
- runs upward, forming an inverted cone as it widely attaches to the undersurface of the clavicle (around the conoid tubercle)
-
trapezoid ligament
- origin: trapezoid ridge on the coracoid process of the scapula
- runs laterally and horizontally, attaching to the underside of the clavicle (to the similarly named, trapezoid ridge)
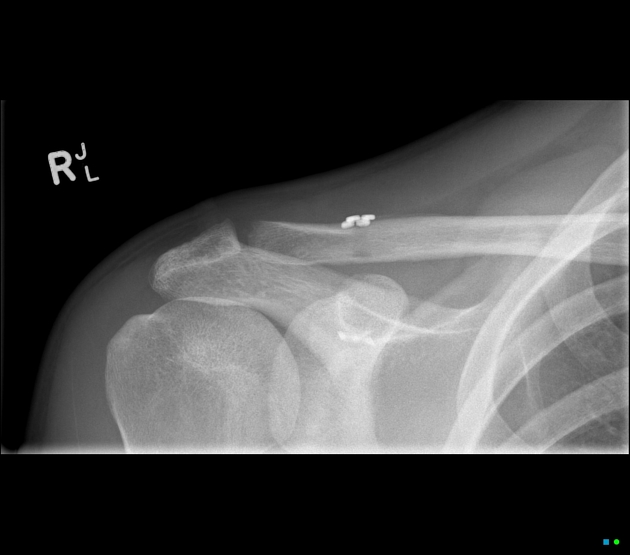
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
The integrity of the coracoclavicular ligament is inferred on plain radiographs by the coracoclavicular distance.
Related pathology
Quiz questions
References
- 1. McMINN. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Acromioclavicular joint injury
- Scapula
- Conoid tubercle
- AO classification of clavicle fractures
- Coracoclavicular distance
- Coracoid process
- Clavicle
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Coracoclavicular bursa
- Trapezoid ligament
- Shoulder ligaments
- Clavipectoral fascia
- Shoulder
- Conoid ligament
- Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury
Cases:
Multiple choice questions:
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centers
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centers
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centers
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.