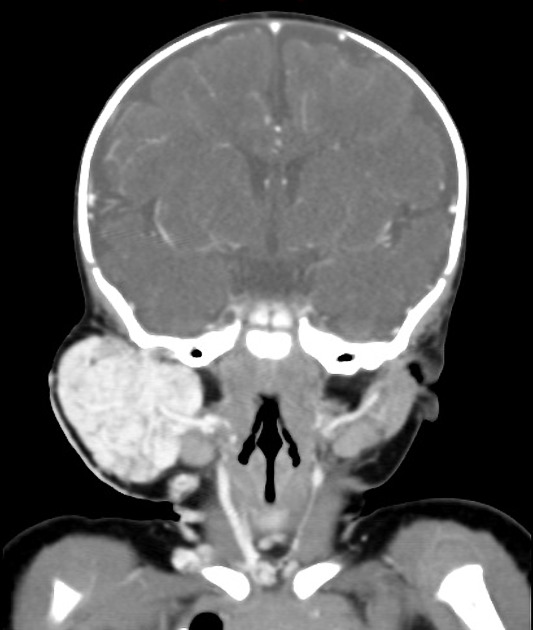
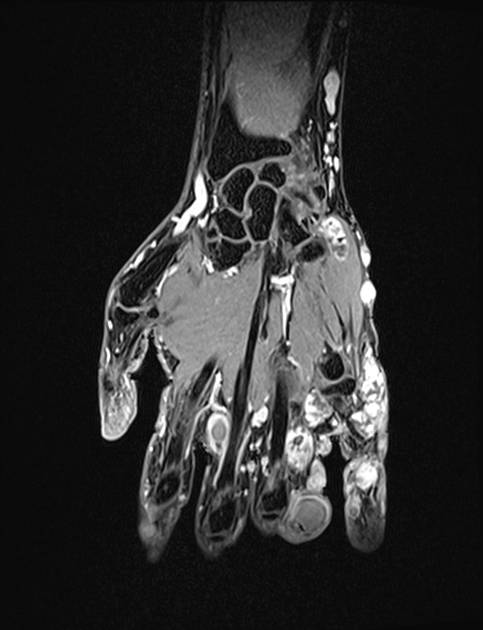
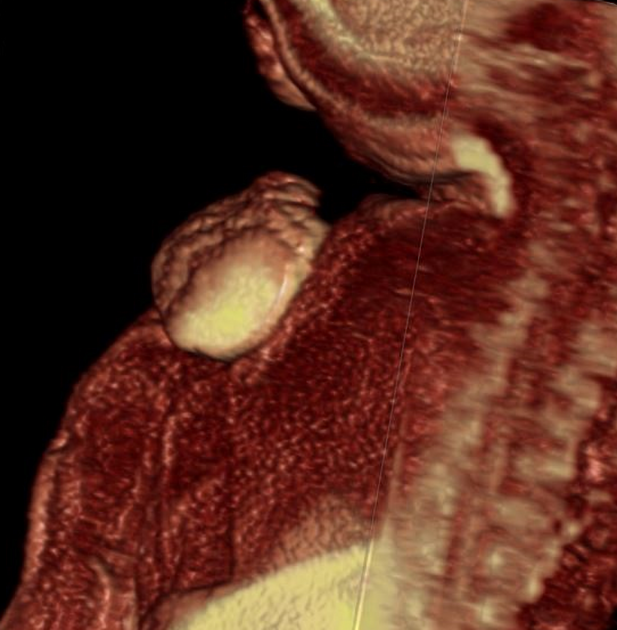
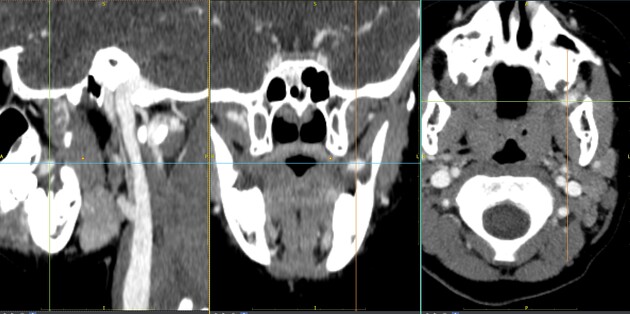
Hemangioma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Donna D'Souza had no recorded disclosures.
View Donna D'Souza's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ashesh Ishwarlal Ranchod had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ashesh Ishwarlal Ranchod's current disclosures- Hemangioma
- Haemangioma (General)
- Haemangioma - general
- Hemangiomas
- Haemangiomas
Hemangiomas are benign tumors of vascular origin, usually seen in early childhood. Though many types exist according to the ISSVA classification, the most common are by far infantile hemangiomas. Other types include congenital hemangiomas, spindle-cell hemangiomas, epithelioid hemangiomas and intramuscular hemangiomas.
Terminology
Unfortunately, the term hemangioma has been widely misused to apply to many non-neoplastic vascular malformations, particularly the common non-neoplastic soft tissue venous malformations and cerebral cavernous venous malformations (cavernomas). Gradually, the everyday nomenclature is catching up to modern classification systems (see ISSVA classification and/or the less used Hamburg classification system), and it is best to avoid the term hemangioma unless referring to the truly neoplastic entities above.
Further discussion is delegated to the vascular malformations and tumors article.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Vilanova J, Barceló J, Smirniotopoulos J et al. Hemangioma from Head to Toe: MR Imaging with Pathologic Correlation. Radiographics. 2004;24(2):367-85. doi:10.1148/rg.242035079
- 2. Haaga, John R. 1945-. CT and MR Imaging of the Whole Body. (2009) ISBN: 9780323053754
- 3. Merrow A, Gupta A, Patel M, Adams D. 2014 Revised Classification of Vascular Lesions from the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies: Radiologic-Pathologic Update. Radiographics. 2016;36(5):1494-516. doi:10.1148/rg.2016150197
Incoming Links
- Macrodystrophia lipomatosa
- Pedunculated intratracheal mass
- Spiculated periosteal reaction
- Bowel wall calcification
- Tumours of the small intestine
- Placental chorioangioma
- Parotid space
- Glomangioma
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Pseudopermeative process in bone
- Retiform haemangioendothelioma
- Angiolipoma
- Mediastinal haemangioma
- Pyriform aperture stenosis
- WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue
- Endobronchial haemangioma
- Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
- Musculoskeletal angiosarcoma
- WHO classification of head and neck tumors
- WHO classification of skin tumours
- Focal nodular hyperplasia and hemangioma
- Intramuscular haemangioma (tongue)
- Giant hepatic haemangioma
- Multifocal intraosseous hemangiomas
- Morel-Lavallée lesions
- Soft tissue venous malformation
- Infantile heamangioma- retromolar space
- Infantile hemangioma
- Congenital intramuscular haemangioma (fetal MRI)
- Haemangioma of the calf
- Large renal angiomyolipoma
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Facial venous hemangioma
- Hepatic hemangioma
- Adrenal hemangioma
- Supraorbital haemangioma
- Soft tissue hemangioma
- Slow flow vascular malformation - knee
- Sublingual hemangioma
- Renal cell carcinoma in horseshoe kidney
Related articles: Pathology: Vascular: Vascular tumours and malformations
-
vascular malformations and tumors
- classifications
- vascular tumors
-
hemangioma
- infantile hemangioma
- congenital hemangiomas (RICH and NICH)
- tufted angioma (with or without Kasabach Merritt syndrome)
- Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (with or without Kasabach Merritt syndrome)
- spindle cell hemangioendothelioma
- other, rare hemangioendotheliomas
- dermatologic acquired vascular tumors
-
hemangioma
- slow-flow vascular malformations
- capillary malformation (CM)
- venous malformation (VM)
- common sporadic venous malformation
-
cavernous venous malformation (cavernoma or cavernous hemangioma)
- cerebral cavernous venous malformation
- orbital cavernous venous malformation
-
hepatic cavernous venous malformation (hepatic hemangioma)
-
atypical hepatic venous malformation (atypical hepatic hemangioma)
- giant hepatic venous malformation (giant hepatic hemangioma)
- flash filling hepatic venous malformation (flash filling hepatic hemangioma)
-
atypical hepatic venous malformation (atypical hepatic hemangioma)
- splenic cavernous venous malformation (splenic hemangioma)
- breast venous malformation (breast hemangioma)
- retroperitoneal venous malformation
- soft tissue venous malformation
- primary intraosseous venous malformation
- cardiac venous malformations
-
cavernous venous malformation (cavernoma or cavernous hemangioma)
- Bean syndrome
- familial cutaneous and mucosal venous malformation
- glomuvenous malformation (glomangioma)
- Maffucci syndrome
- common sporadic venous malformation
- lymphatic malformation (LM)
- fast flow vascular malformations
- arterial malformation
- ectasia
- coarctation
- aneurysm
- arterial malformation
- arteriovenous fistulae (with one or more shunts)
- arteriovenous malformations (with a nidus of multiple shunts)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.