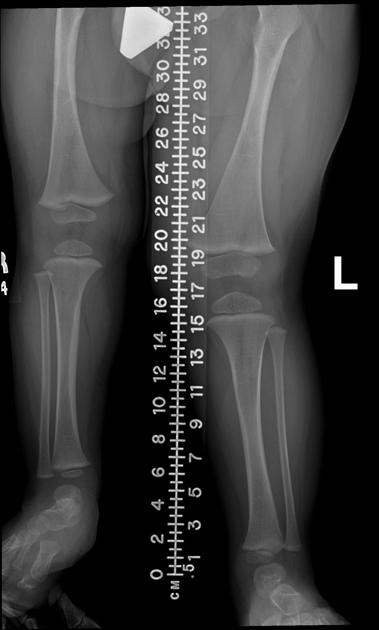
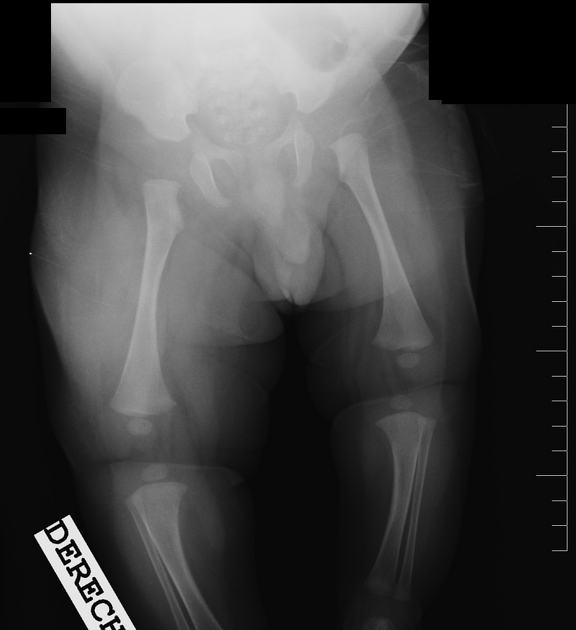
Hemihyperplasia, also known as hemihypertrophy, is asymmetry in size between the right and left of the body, more than can be attributed to normal variation.
On this page:
Article:
Images:
Images:
Terminology
Hemihyperplasia is more scientifically correct than hemihypertrophy as the cells are hyperplastic rather than hypertrophied 1.
Epidemiology
Incidence is estimated at 1 in ~50,000 live births 2,4.
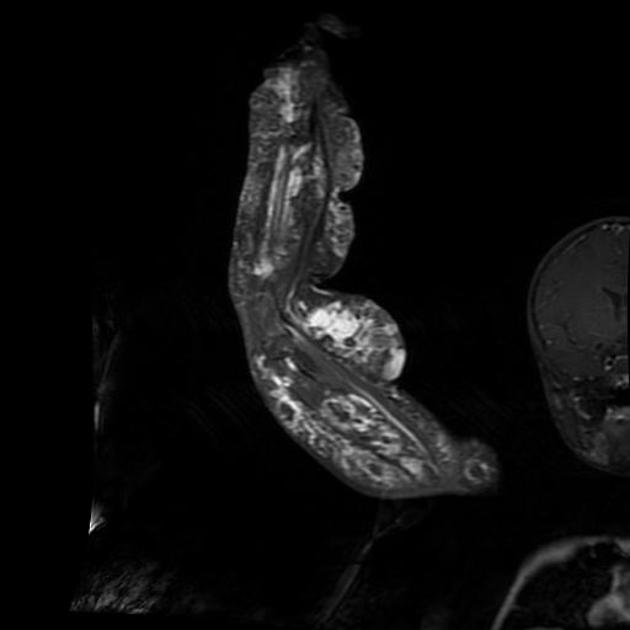
Pathology
Etiology
Hemihyperplasia can arise sporadically as isolated hemihyperplasia, or it can arise as part of a syndrome 2-4:
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Proteus syndrome
- Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome
- neurofibromatosis type 1
- Hemihyperplasia-multiple lipomatosis (HHML)
- McCune Albright Syndrome
- Langer Giedeon Syndrome
Associations
Increased risk (5% of patients) of malignancy, most commonly Wilms tumors 2.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.