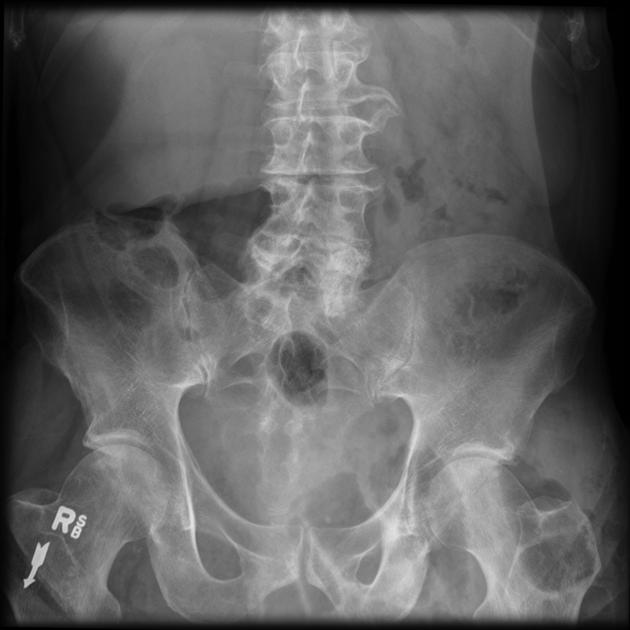
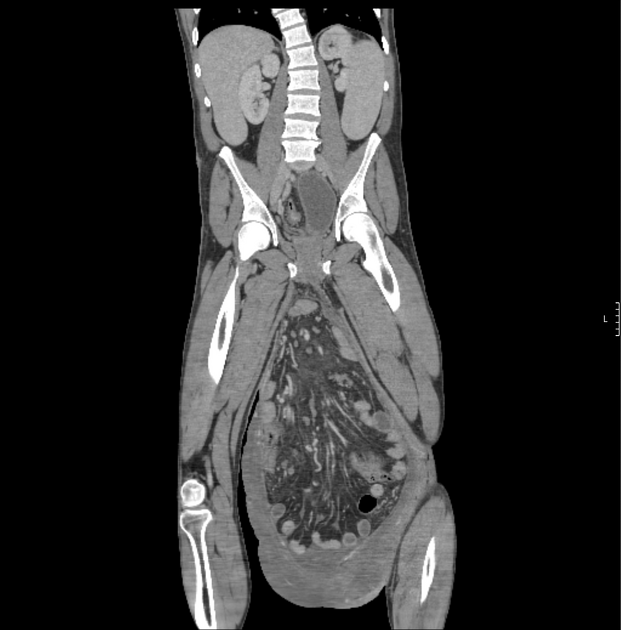
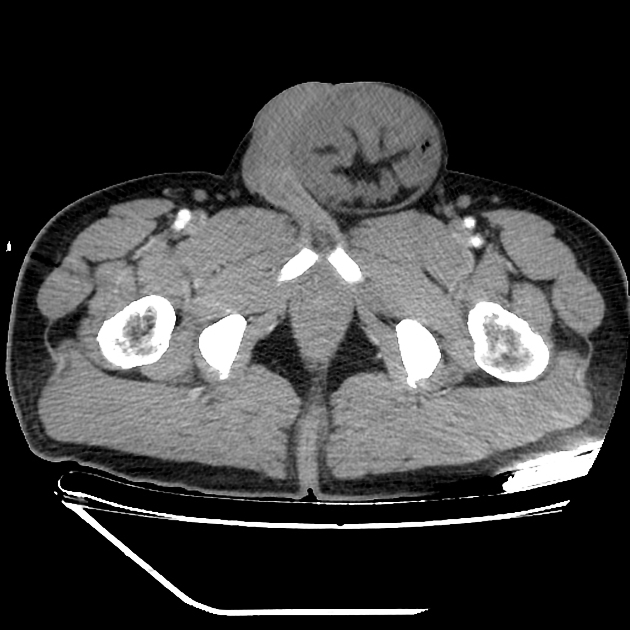
Inguinal hernias (herniae also used) is the type of groin herniation (part of the larger group of abdominal wall hernias) that occurs above the inguinal ligament and through the inguinal canal.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Inguinal hernias are the commonest type of abdominal wall hernias (up to 80% 3) and are most often acquired. There is a recognized male predilection with an M:F ratio of up to 7:1 3.
Clinical presentation
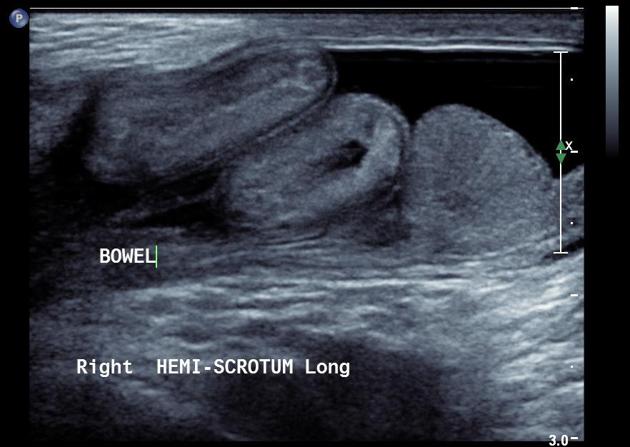
Patients most commonly present with swelling and/or pain in the relevant groin, iliac fossa, loin. Men may also have testicular pain.
Pathology
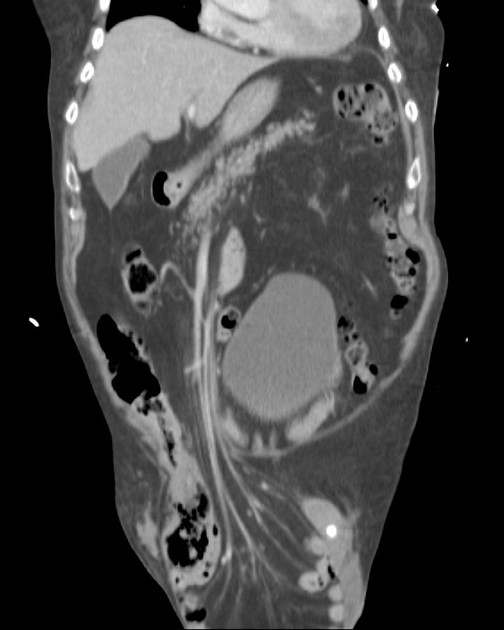
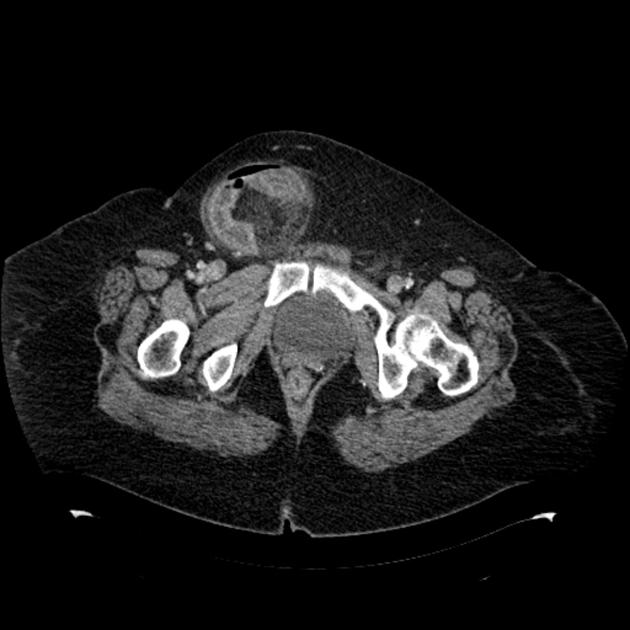
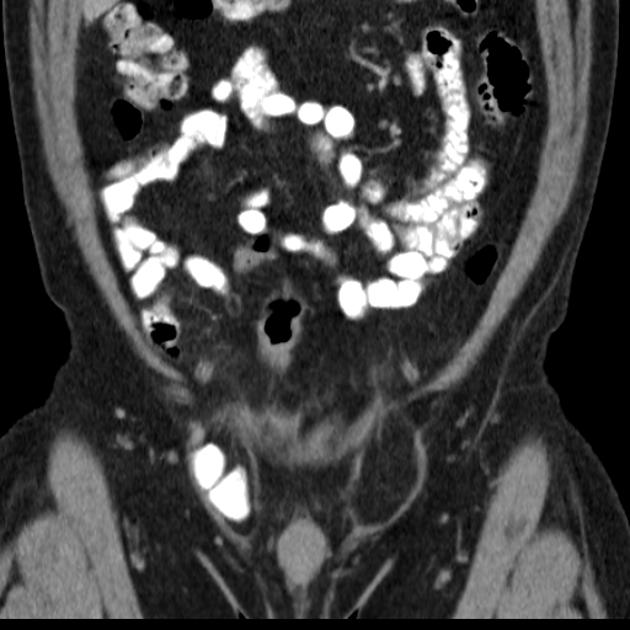
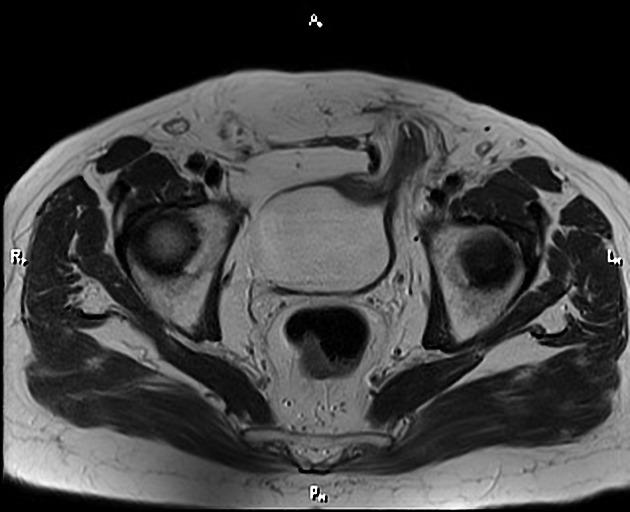
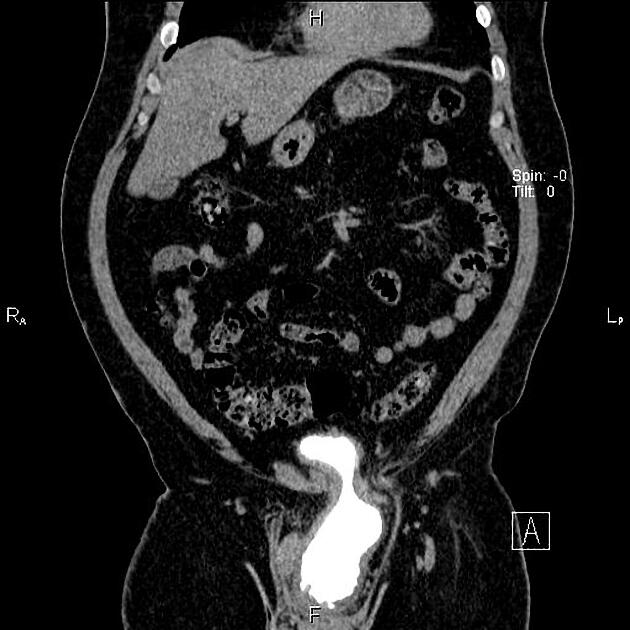
Classification
It is broadly divided into two types:
-
indirect inguinal hernia (more common)
herniates lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels 2
passes through the deep inguinal ring
anterior to the spermatic cord in males 8
follows the round ligament in females 8
-
direct inguinal hernia (less common)
herniates medial to the inferior epigastric vessels 2
passes through a defect in the Hesselbach triangle
a weakness in the fascial floor of the inguinal canal 10
A combination of ipsilateral direct and indirect inguinal herniae is a special type of pantaloon hernia and given the term Romberg hernia.
Etiology
All of the following confer an increased risk for indirect inguinal hernia:
prematurity and low birth weight 9
patent processus vaginalis
urologic conditions, e.g. cryptorchidism, hypospadias or epispadias, bladder exstrophy, ambiguous genitalia
abdominal wall defects (omphalocele, gastroschisis, cloacal exstrophy, bladder exstrophy)
family history
A direct inguinal hernia is a consequence of weakened abdominal musculature, often brought on by
advanced age
strain
previous abdominal surgery
While inguinal hernias, in general, are much more common in males than in females, direct hernias, in particular, are rare in women since the broad ligament acts as an additional barrier.
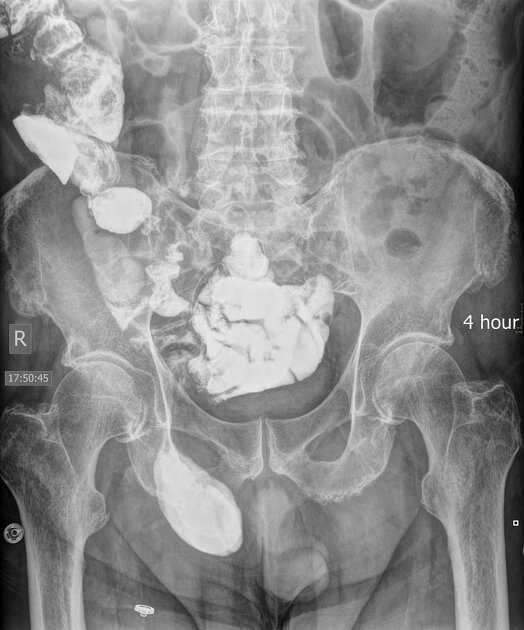
Treatment and prognosis
Surgical treatment options include
Complications
Complications, as in any other abdominal wall herniation, include:
Compared with other types of abdominal wall hernias, the incidence of complications is considered lower 3.
Differential diagnosis
Possible imaging differential considerations include
femoral hernia: often remain lateral to the pubic tubercle and compress the femoral vein
hydrocele (may coexist)
spermatic cord hematoma




















 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.