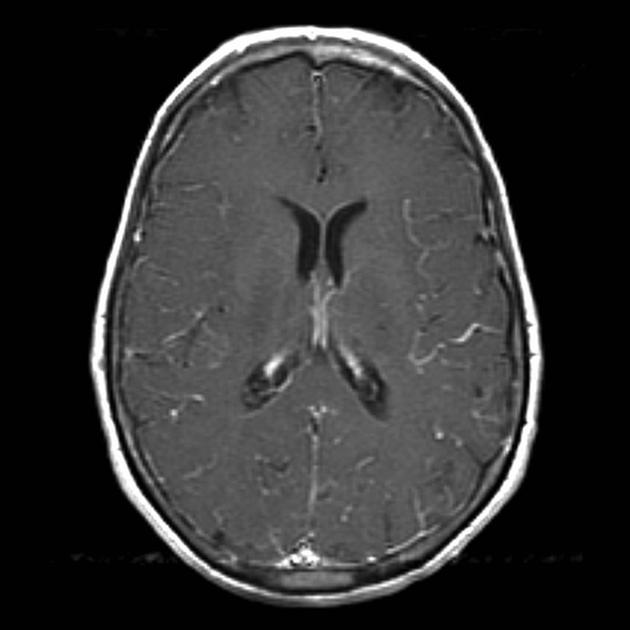
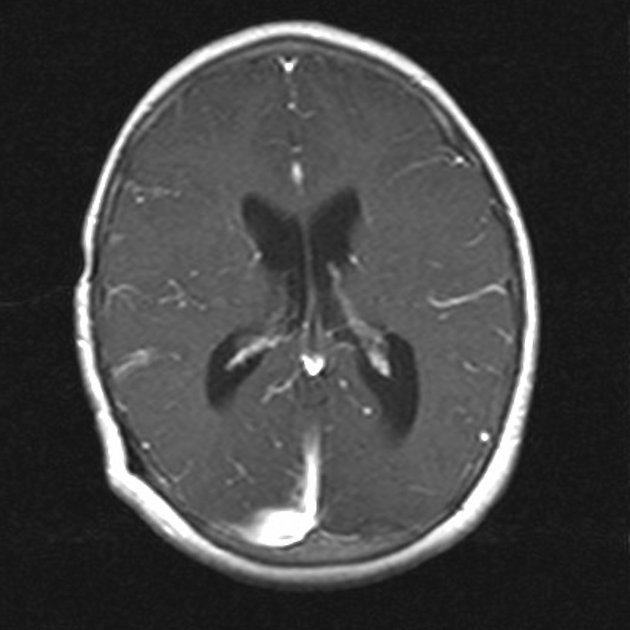
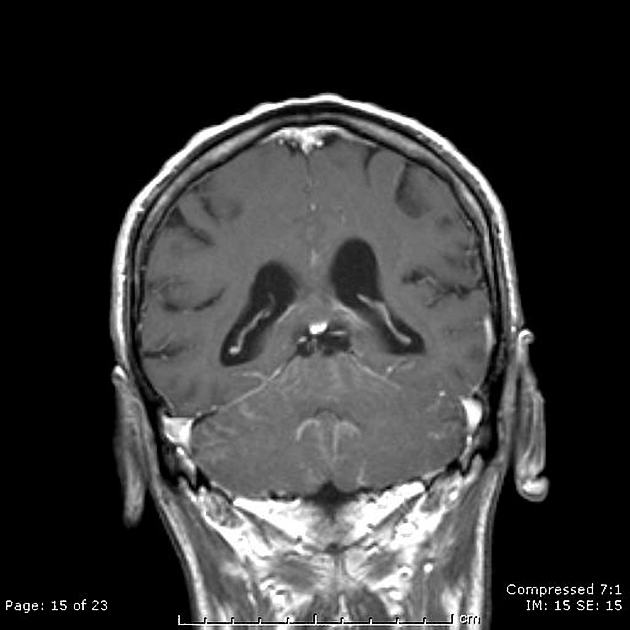
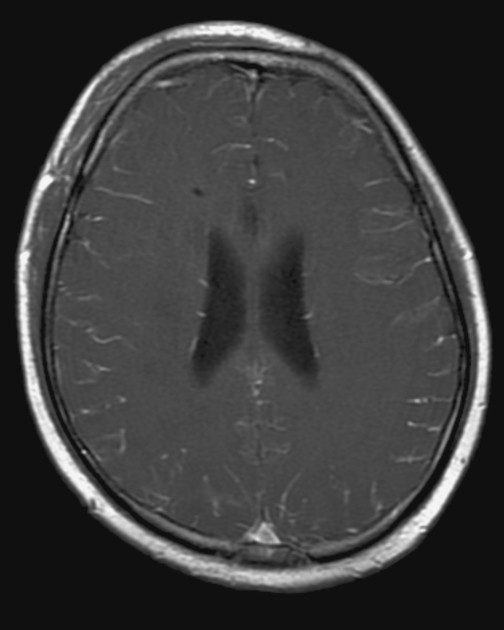
Leptomeningeal enhancement refers to a diffuse or focal gyriform or serpentine enhancement that can be seen in the following conditions:
Diffuse
-
tuberculous meningitis (can also be focal)
coccidioidal meningitis (can also be focal)
-
-
primary
-
secondary
leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (e.g. from carcinoma of breast or lung, melanoma, ependymoma)
-
hemorrhage (e.g. post-subarachnoid)
post uncomplicated lumbar puncture (rare, less than 5%) 2
-
granulomatous conditions
neurosarcoidosis (can also be focal)
post-operative (late finding)
post-traumatic (late finding)
Focal
leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (e.g. from carcinoma of breast or lung, melanoma)
post-ictal hyperemia
ischemic stroke: subjacent acute (leptomeningeal collaterals) or subacute
meningitis (e.g. tuberculous)
postoperative scar
Terminology
The enhancement of the brain surface is known as pial or pial-arachnoid enhancement and often referred to as leptomeningeal enhancement 3.
Conversely, as the thin arachnoid membrane is attached to the inner surface of the dura mater, the pachymeningeal pattern of enhancement can also be described as a dural-arachnoid enhancement 3.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.