Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type IIa, also known as Sipple syndrome, accounts for most cases of MEN2 and is characterized by:
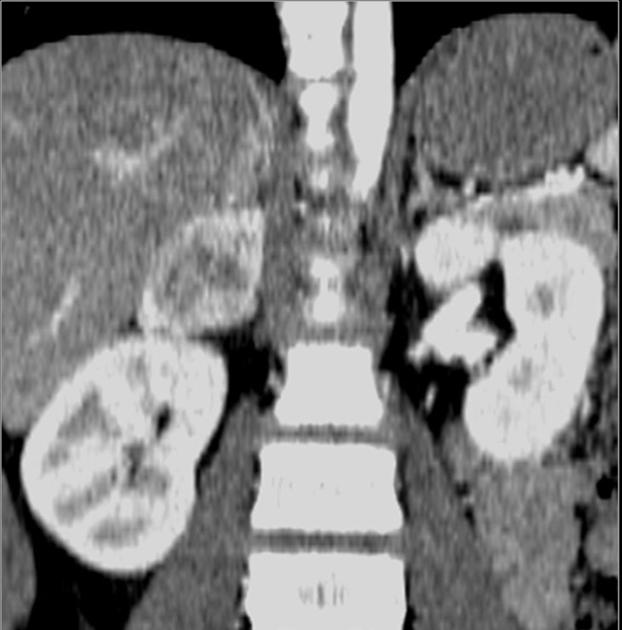
pheochromocytomas: in 50% of patients, often bilateral, and can be extra-adrenal
medullary thyroid cancer (MTC): 100% of patients, aggressive, and may secrete calcitonin
parathyroid hyperplasia: only seen in 20% of patients, and often presents with hypercalcemia and renal calculi
Mnemonic:
PMP
On this page:
Epidemiology
The estimated prevalence of MEN2a is about 1 per 50,000 4.
Pathology
MEN2a is subdivided into 4 groups 4:
Classical MEN 2A associating MTC, pheochromocytoma and primary hyperparathyroidism
MEN 2A associated with cutaneous lichen amyloidosis
MEN 2A associated with Hirschsprung disease
familial MTC (FMTC)
Genetics
A small proportion of individuals have a RET D631 proto-oncogene mutation. RET mutation is different from the RET translocation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. The chromosome locus is 10q11.2. 3




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.