Oligohydramnios
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
Oligohydramnios refers to a situation where the amniotic fluid volume is less than expected for gestational age. Often these fetuses have < 500 ml of amniotic fluid.
Epidemiology
The estimated prevalence can be up to ~6% of pregnancies 4.
Pathology
Causes
The causes of oligohydramnios are protean and one way to simplify it is by using the following mnemonic: DRIPPC
-
D:
- demise
- drugs: e.g
protaglandinprostaglandin inhibitors(Indomethacin(indomethacin)
-
R:
-renalrenal abnormalities (from decreased urine output) -
I:
- IUGRIUGR (intra-uterine growth restriction):- 80%: maymay occur from decreased renal perfusion due to sparing effect - P: premature rupture of membranes
- P: post dates
- C: chromosomal anomalies (especially if other anomalies are found)
Associations
- Potter sequence
- underlying fetal hypoxia and fetal cardiovascular compromise: from preferential flow to the fetal brain at the expense of renal shut down
- twin pregnancy related complications:
- twin to twin transfusion syndrome: in pump twin
- maternal dehydration
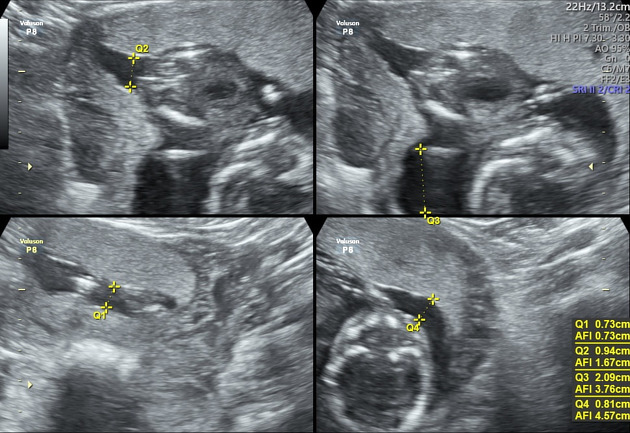
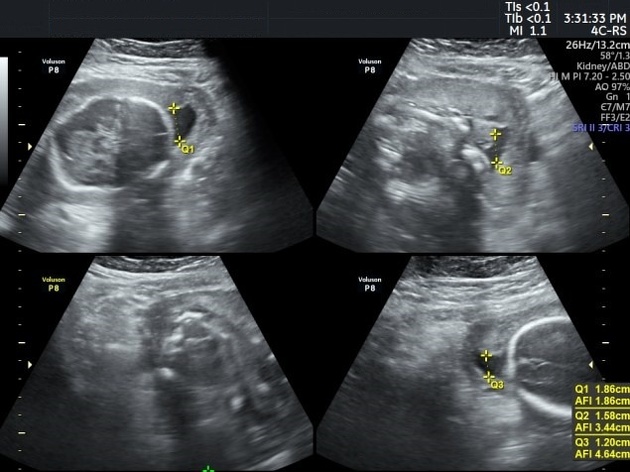
Radiographic assessment
Antenatal ultrasound
Several sonographic criteria can be used which include:
- four quadrant amniotic fluid index (AFI): < 5
- two diameter pocket method: < 1 x 1 cm or < 15 cm2
- maximum vertical pocket depth: < 2 cm
Complications
- first trimester oligohydramnios can result in failure of pregnancy in up to 95% from complications such as:
- pulmonary hypoplasia: implies a very poor prognosis
- fetal limb contractures
Treatment and prognosis
Development of oligohydramnios early is pregnancy is generally a poor prognostic marker. An amnio-infusion can be carried in severe cases in the appropriate situation.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.