A subcutaneous abscess is a kind of soft tissue abscess and a manifestation of a spectrum of skin and soft tissue infections which also includes cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis. It is a form of abscess which lies within the dermis and subdermal cutaneous layers. Along with dental abscesses, the subcutaneous layer is the most common site for abscess formation.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Patients typically present with an acute or subacute history of a focal swelling or lump in the affected skin with accompanying signs of cellulitis. If there is bacteremia, the patient may present with systemic signs of sepsis such as fever, rigours, and raised inflammatory markers.
Pathology
Skin abscesses are overwhelmingly caused by bacteria that spread into the subcutaneous tissues through breaches in the epidermis. Streptococcus species have traditionally been the most common pathogens. Fungal abscesses are rare.
In some cases sterile abscess formation has been described where an irritant drug or substance is injected into the skin, resulting in aseptic inflammation and abscess formation.
Radiographic features
Subcutaneous abscesses are usually diagnosed clinically and do not routinely require any imaging. In complex cases where possible radical surgical treatment is being considered imaging may be undertaken to determine the extent of soft tissue involvement. MRI is the preferred modality for the evaluation of more deep soft tissue abscesses 4.
Ultrasound is being shown to be increasingly useful for differentiating cellulitis with gross cutaneous swelling from a true abscess, with one study reporting that ultrasound evaluation changed management in half of all emergency cases of cellulitis 3.
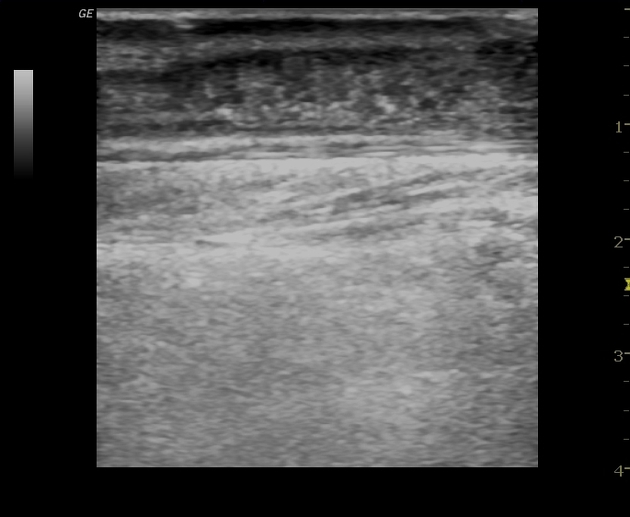
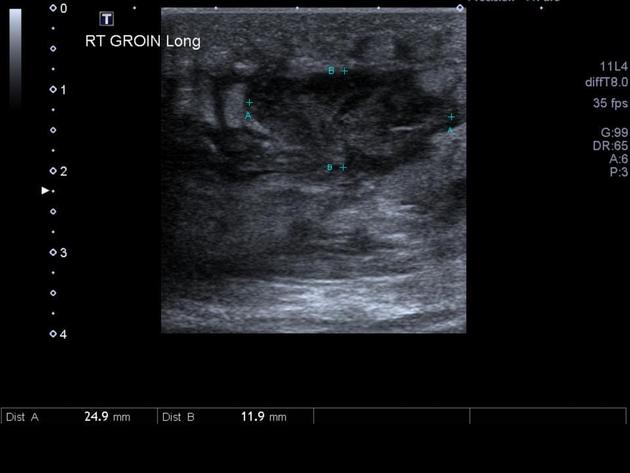
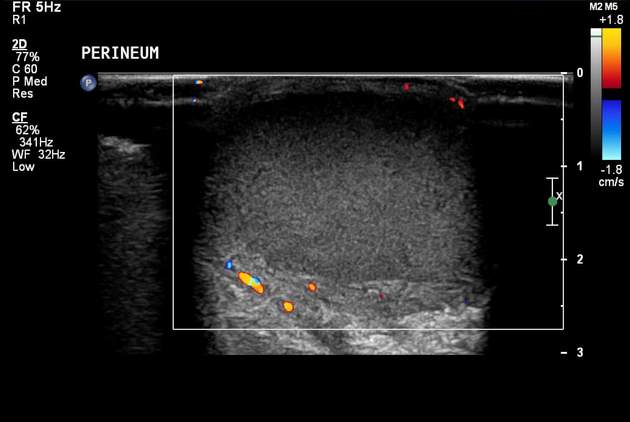
Ultrasound
anechoic or hypoechoic spherical collections of echogenic fluid
there may be an echogenic capsule but often the borders are poorly defined
septa, sediment, or even gas may be seen within the central fluid collection
compression with the transducer may induce movement or swirling of the abscess contents
cobblestone appearance of surrounding subcutaneous tissues due to edema from associated cellulitis
Differential diagnosis
Possible imaging differential considerations include
herniated bowel
blood vessel




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.