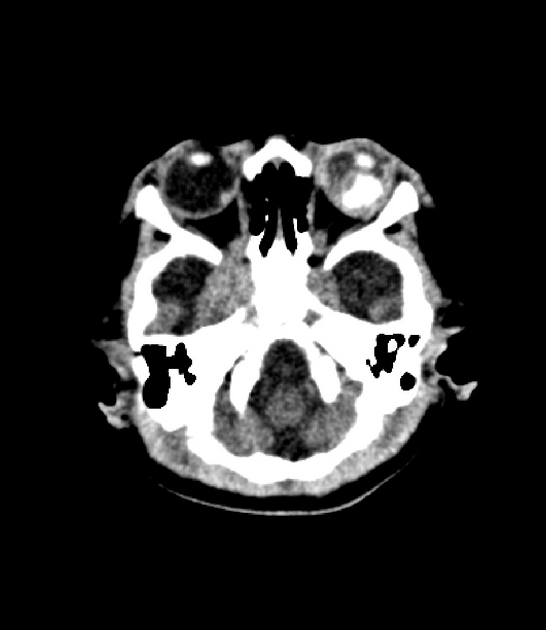
Trilateral retinoblastoma refers to the combination of retinoblastoma (usually bilateral) and pineoblastoma. This association highlights the close relationship between these highly aggressive small round blue cell tumors.
The clinical presentation, pathology and radiographic appearances are those of retinoblastomas and pineoblastomas. The pineoblastoma is usually located in the pineal gland but can on occasion be seen in the suprasellar region.
Epidemiology
It affects only a minority of patients with retinoblastoma (1.5-5%) and is almost always seen in children with bilateral retinoblastoma; in this subset of patients, the rate may be as high as 25%.
Treatment and prognosis
Prognosis is guarded even with aggressive surgery, high dose chemotherapy and radiotherapy 2. CSF seeding is common, with a dismal prognosis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.