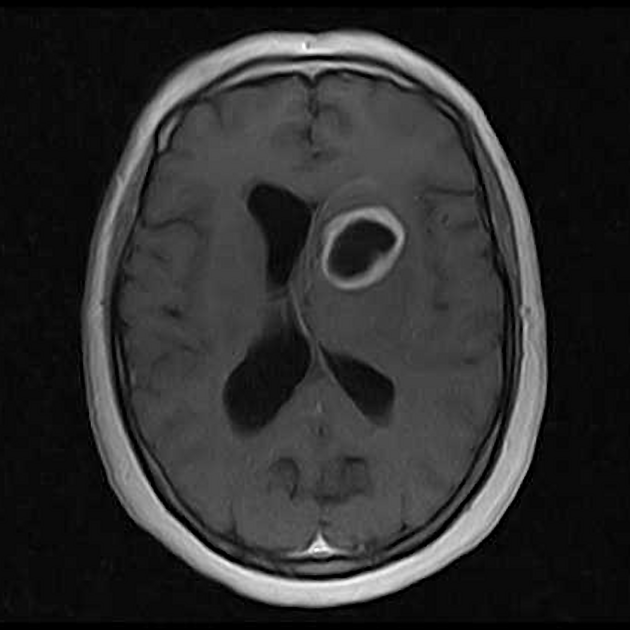
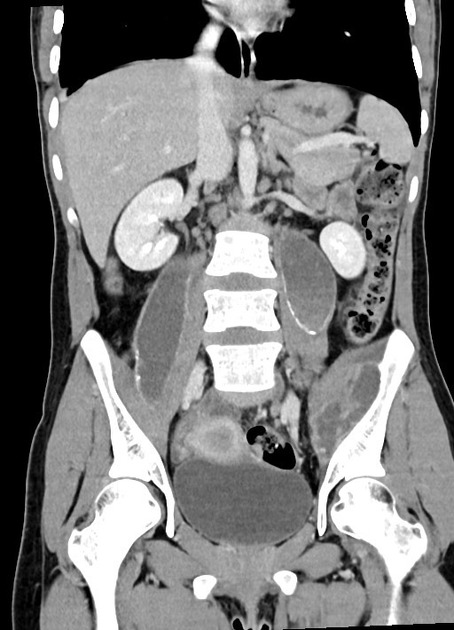
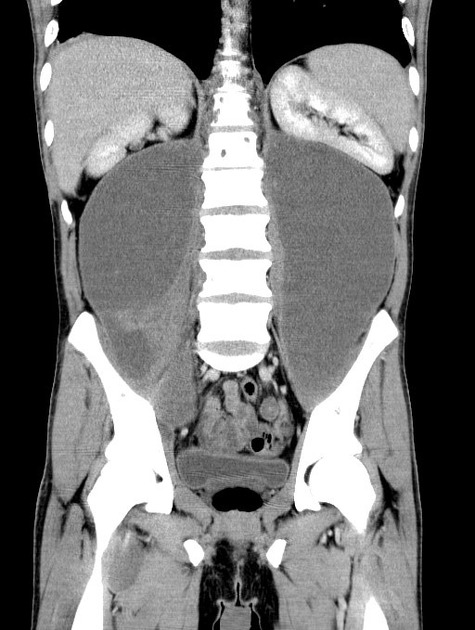
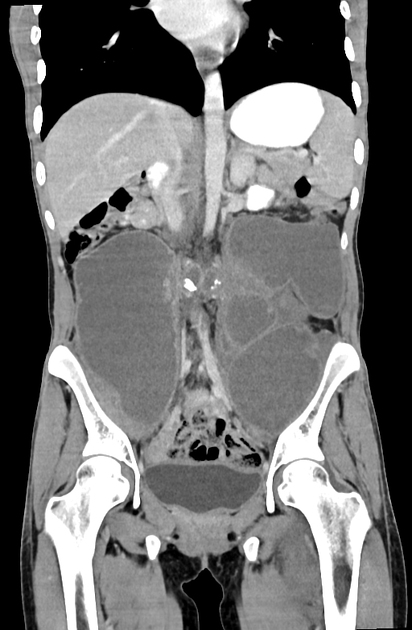
Tuberculous abscess
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Liz Silverstone had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Liz Silverstone's current disclosures- TB abscess
- TB abscesses
Tuberculous abscesses are an uncommon presentation of tuberculosis, most often encountered in immunocompromised individuals (e.g. HIV/AIDS). Unlike the far more common tuberculomas (tuberculous granulomas), tuberculous abscesses contain pus with abundant identifiable organisms 1. The capsule that surrounds the necrotic purulent core is similar to more common bacterial abscesses, lacking the granulomatous reaction prominent in tuberculomas 1. They also lack the pus and neutrophils usually present in pyogenic abscesses 2. Spectroscopy usually shows lactate and lipid peaks 2.
Terminology
The medical literature documents several phenomena described as tuberculous abscesses including intracranial tuberculous abscesses, dermal abscesses (a.k.a. gummas), and metastatic tuberculous abscesses.
References
- 1. Frangoise Gray, Charles Duyckaerts, Umberto De Girolami. Escourolle and Poirier's Manual of Basic Neuropathology. ISBN: 9780199929054
- 2. Anne G. Osborn, Gary L. Hedlund, Karen L. Salzman. Osborn's Brain. (2017) ISBN: 9780323477765
- 3. Sezgin B, Atilganoglu U, Yigit O, Ergün SS, Cambaz N, Demirkesen C. Concomitant cutaneous metastatic tuberculous abscesses and multifocal skeletal tuberculosis. (2008) Indian journal of dermatology. 53 (3): 149-53. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.43208 - Pubmed
- 4. Troelsen, Thomas, Hilberg, Ole. Tuberculous Abscess. (2014) The New England journal of medicine. 371 (2): 161. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1311878 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Disseminated TB - lung, liver abscess, cutaneous fistula
- Tuberculous arthropathy - wrist
- Tuberculous spondylitis
- Tuberculous spondylodiscitis with bilateral calcified psoas abscesses
- Pott disease
- Tuberculous spondylitis (Pott disease)
- Giant cerebral tuberculoma
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis
- Pott's disease
- Tuberculous spondylitis
- Tuberculous spondylitis (Pott disease) with large psoas abscesses
- Extensive Pott disease with large psoas muscles abscesses
- Tuberculous spondylitis
- Disseminated tuberculosis with spondylitis (Pott disease) and massive iliopsoas abscesses
- Severe Pott disease with multiple muscular and subcutaneous abscesses
- Cervicothoracic cold abscess - tuberculosis
- Tuberculous mycotic abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Tuberculous abscess
- Chest wall abscess: tubercular
Related articles: Infections
- bacterial
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus anginosus group
- Staphylococcus aureus
- group A Streptococcus
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- atypical
-
tuberculosis
- causative agent
- tuberculoma (tuberculous granuloma)
- tuberculous abscess
- miliary tuberculosis
- pulmonary tuberculosis
-
extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- intracranial tuberculosis
- tuberculous otomastoiditis
- tuberculous lymphadenopathy
- cardiac tuberculosis
- tuberculous mastitis
-
abdominal tuberculosis
- gastrointestinal tuberculosis
- tuberculous peritonitis
- visceral tuberculosis
- hepatic tuberculosis
- gallbladder tuberculosis
- pancreatic tuberculosis
- splenic tuberculosis
-
genitourinary tuberculosis
- renal tuberculosis
- bladder and ureteric tuberculosis
- prostatic tuberculosis
- scrotal tuberculosis (testes, epididymis, seminal vesicles, vas deferens)
- tuberculous pelvic inflammatory disease (female)
- skeletal tuberculosis
-
tuberculosis
- viral
- fungal
- Aspergillus
-
aspergillosis
- CNS aspergillosis
-
fungal sinusitis
- non-invasive: hyphae do not invade mucosa
- invasive: hyphae seen invading mucosa +/- beyond
- pulmonary aspergillosis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.