Presentation
Progressive left side proptosis without pain but impaired visual acuity.
Patient Data
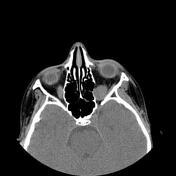

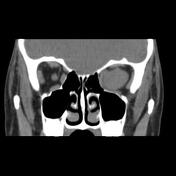

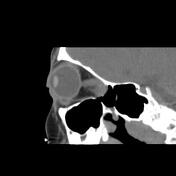

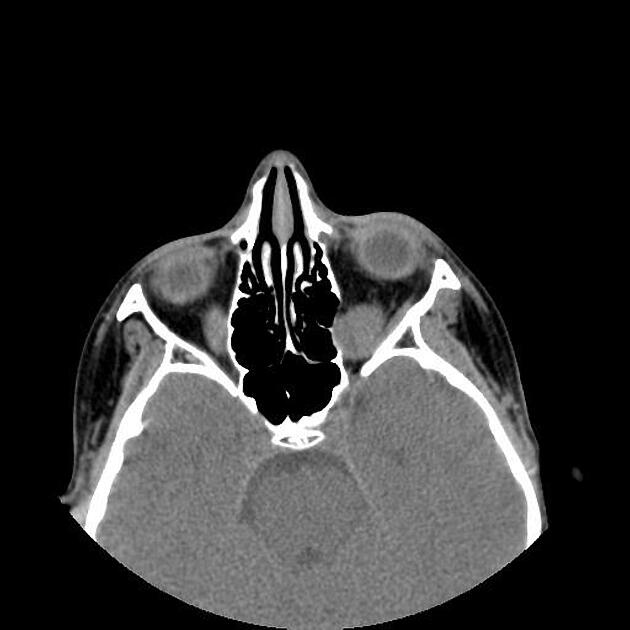
A well-defined solid appearing mass lesion with axial width up to 20 x 18 mm and the height of up to 15 mm within the left orbital apex interposed the inferior and temporal side of the optic nerve sheath complex and superior rectus muscle, inferior rectus muscle, and lateral rectus muscle with impression on the optic nerve and the mentioned extraocular muscles is seen. Left side proptosis, the compression of the mass on the related posterior medial orbital wall, and adjacent superior orbital fissure widening.
Case Discussion
The case illustrates non-contrast MDCT features of pathology-proved schwannoma of the orbital cavity. Orbital apex schwannoma can lead to compressive optic neuropathy, scotomas, and impaired visual acuity but diplopia is a rare occurrence 1. The main treatment is complete surgical excision if feasible and the tumor has a very low rate of recurrence 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.