Presentation
Epigastric pain.
Patient Data

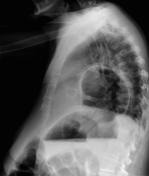
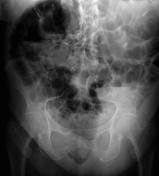
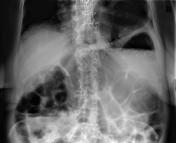
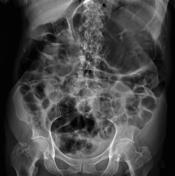
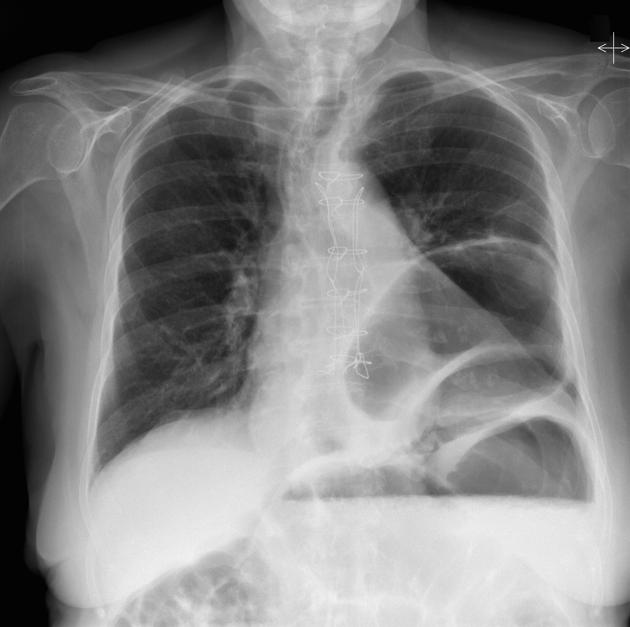
Abdominal & chest x-rays show diffuse distension of bowel loops (colon & small bowel), as well as a hiatal hernia. The hiatal hernia shows an unusual loop configuration. The stomach is distended. There is an air-fluid level at the LUQ. No free air.
The findings are non-specific. Ileus? gastric volvulus? CT scan is recommended.
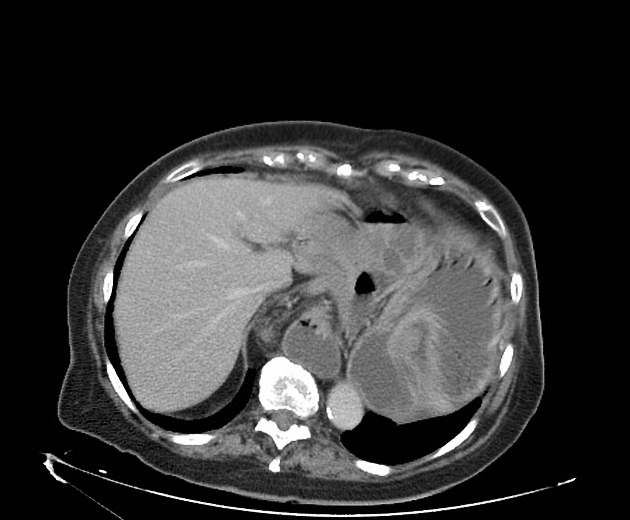
CT scan shows a hiatal hernia and a gastric antrum located superior to the esophagogastric junction, associated with significant gastric distension. Moreover, there is a small fluid accumulation near the diaphragmatic hiatus. No free air. The findings are highly suggestive of a mesentero-axial volvulus.
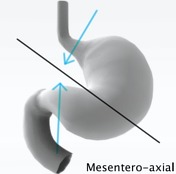
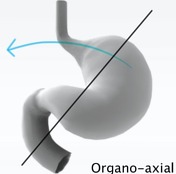
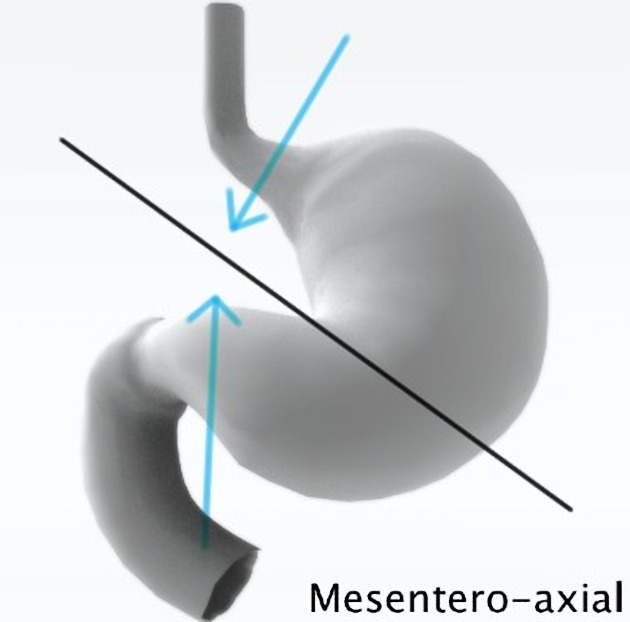
These diagrams show the difference in the mechanism of formation in both types of gastric volvulus.
Author: Maxime St-Amant
License: CC-NC-BY-SA
Case Discussion
This patient presented with the classic Borchardt's triad consisting of :
- inability to pass a nasogastric tube
- severe epigastric pain
- retching without vomiting
The diagnosis of mesentero-axial gastric volvulus was confirmed per-operatively, although it can be hard to distinguish from an organo-axial volvulus.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.