Presentation
Loss of weight. Cough.
Patient Data

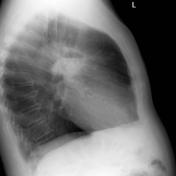
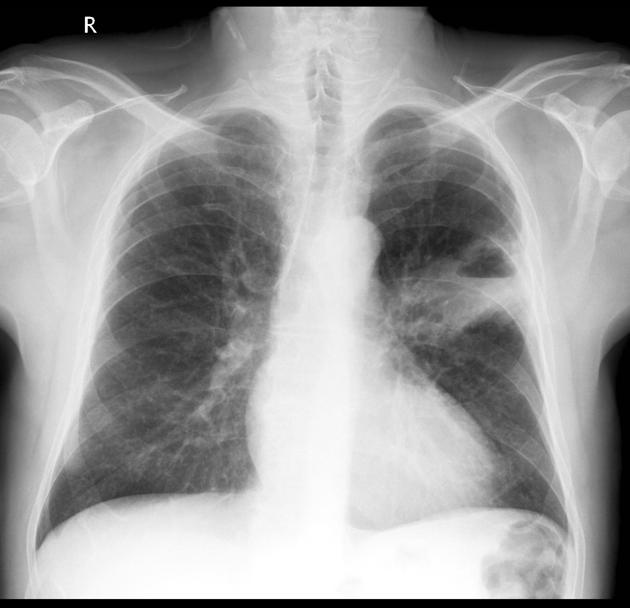
There is a large cavitating mass in the left upper lobe adjacent to the oblique fissure. The prominent air-fluid level is best seen on the lateral radiograph.

Irregular opacity (yellow dotted line) has a central air density lucency (red dotted line) with a horizontal inferior margin (blue arrows) consistent with an air-fluid level, indicative of cavitation.
Case Discussion
This patient has a solitary cavitating mass with an air-fluid level. It is peripheral and therefore likely to be out of the reach of the bronchoscopist.
The patient went on to have CT and biopsy that confirmed the presence of a squamous cell lung cancer.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.