Presentation
Seizures, mental retardation.
Patient Data
Age: 12 years
From the case:
Tuberous sclerosis with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma












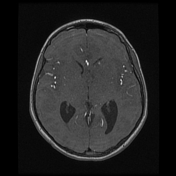

Download
Info
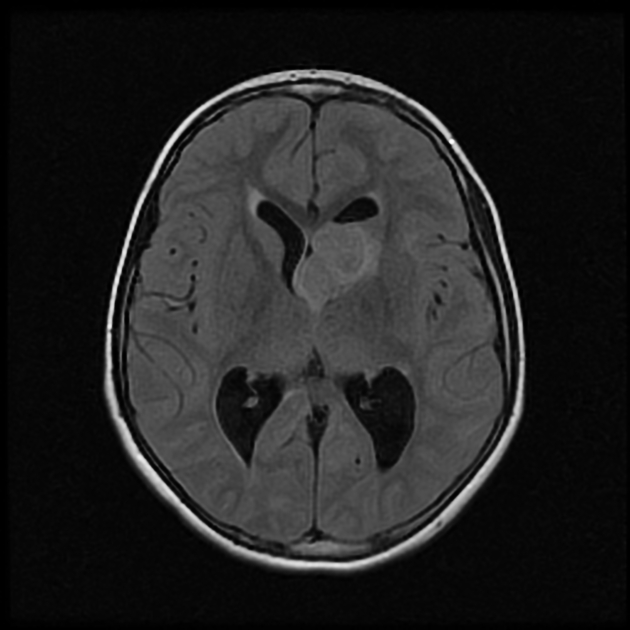
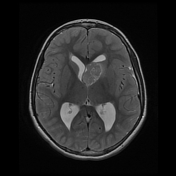
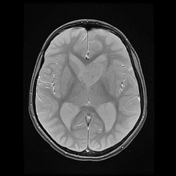
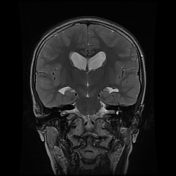
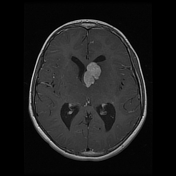
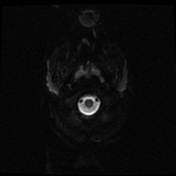
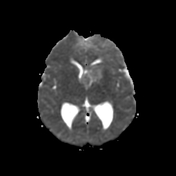
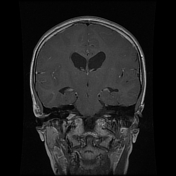
MRI demonstrates a large lobulated intensely enhancing mass arising from the left foramen of Monro causing mild hydrocephalus. Please note the subependymal nodules (best appreciated in the susceptibility weighted sequences), and the subtle hyperintensities in the occipital lobe representing a nice example of cortical/subcortical tubers of tuberous sclerosis (best appreciated on FLAIR).
From the case:
Tuberous sclerosis with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
Download
Info
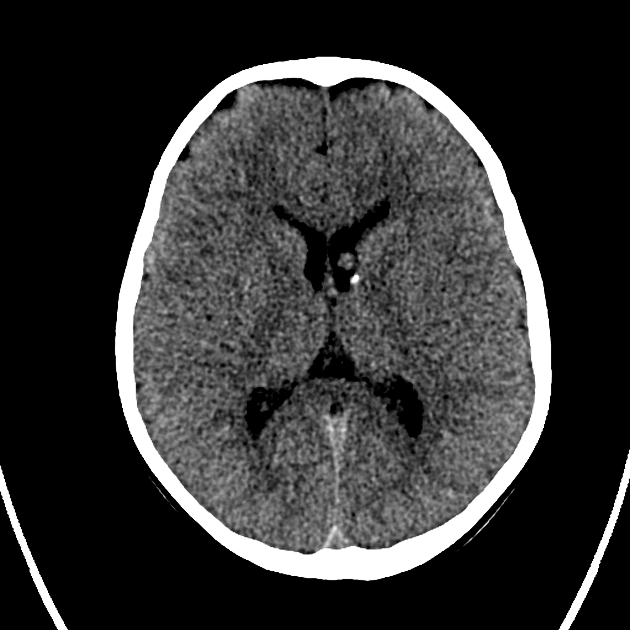
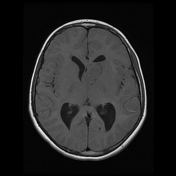
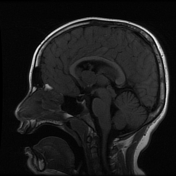
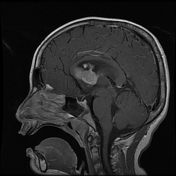
Same patient four years earlier.
Case Discussion
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma is:
- WHO grade I
- the most common CNS neoplasm in tuberous sclerosis (up to 15% of patients with TSC, and rarely (if ever) arises in absence of tuberous sclerosis)
- typically occurs during the 1st two decades




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.