Presentation
Young patient with embolic occipital lobe infarcts. Incidental chest x-ray finding leading to CT chest, which revealed a right apical mass. TB markers negative.
Patient Data
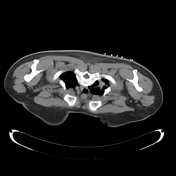

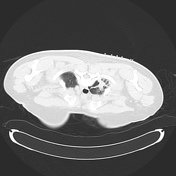

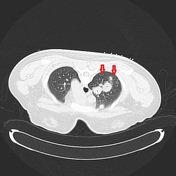
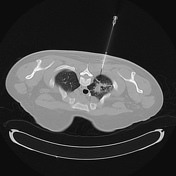

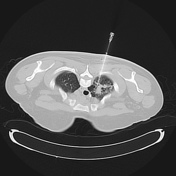

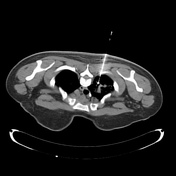

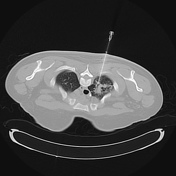

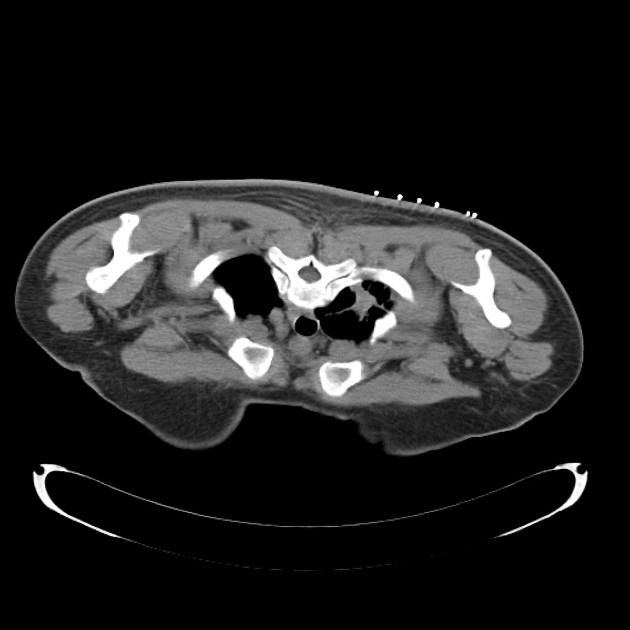
The steps of the biopsy:
1. surface markers to review the target lesion and plan approach - note the oblique fissure at the site of the most appealing place to biopsy - hence this was avoided and the core was taken higher at the apex
2. co-axial needle in position before pleural breech (check course remains ideal)
3. pre-biopsy co-axial needle position
4. post-biopsy pneumothorax check (no pneumothorax is present)
Case Discussion
This case is to illustrate some key technical aspects of a CT guided lung biopsy:
perform only with a good clinical indication
spend time to study and make your own opinion of the diagnostic scan before biopsy
-
avoid traversing fissures, as this increases pneumothorax risk
in this case, an easier route to a larger part of the mass is tempting, but this would traverse the oblique fissure
perform post procedure on table imaging to see if there is any pneumothorax post-procedure




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.