Single contrast enema reduction of colocolonic intussusception
Presentation
Referral from pediatric surgery clinic complaining of abdominal cramps and passing bloody stool three days after an acute attack of pharyngitis
Patient Data
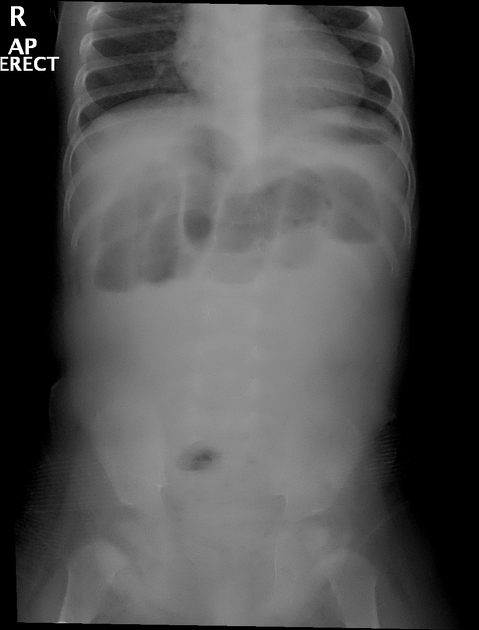
Initial radiographic image demonstrates multiple proximal bowel air fluid levels and gasless distal bowel loops.
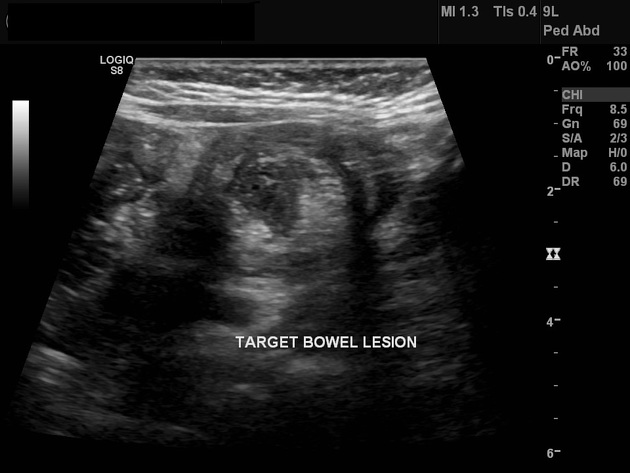
Emergency ultrasound revealed target (or donut) sign of large bowel at the left iliac fossa.
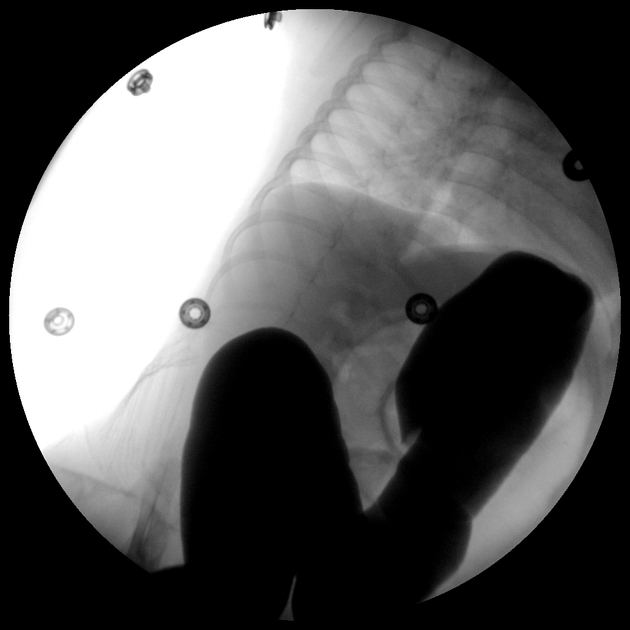
Successful hydrostatic reduction of colocolonic intussusception by a single contrast enema.
At follow up visits, the patient was completely normal.
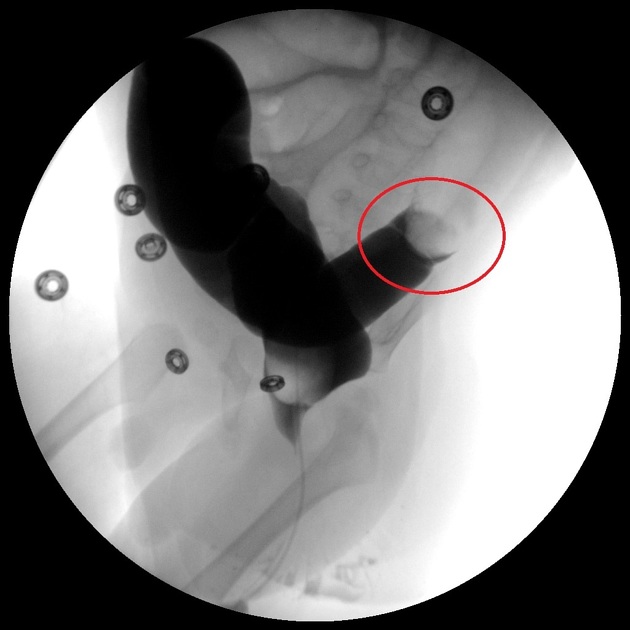
Claw sign highlighted in red circle.
Case Discussion
Hydrostatic reduction of intussusception is done either by single contrast enema or air enema, which is considered safer. In this case, Gastrografin contrast (50/50 concentration with normal saline) was used instead of barium contrast.
The study succeeded to relieve the bowel telescoping and contrast reached the ascending colon.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.