Presentation
Known background of Crohn's disease with persistent abdominal pain and weight loss.
Patient Data
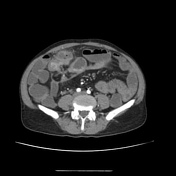

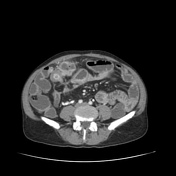

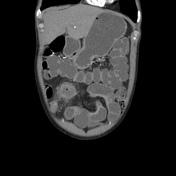



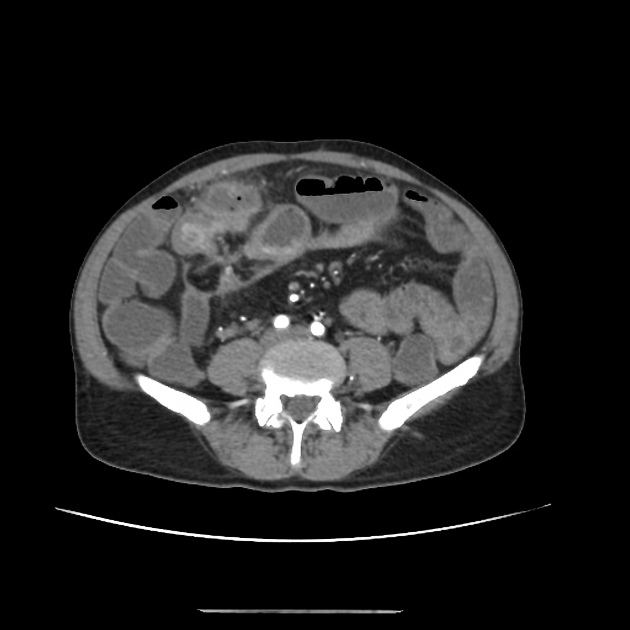
Long-segment circumferential mural thickening and stratification seen involving the mid-ileum with a focal area of two different portions of the inflamed loop communicating with a mesenteric well-defined walled-off abscess. Small microabscesses also seen along the mesenteric margin of the inflamed loop.
Case Discussion
Enteric fistulations and abscess formations are common complications encountered in inflammatory bowel disease. Using neutral contrast enables clear delineation of tracks, extent of inflammation and skip lesions.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.