Presentation
Chorea for investigation.
Patient Data
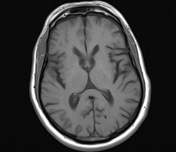

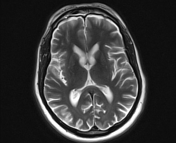

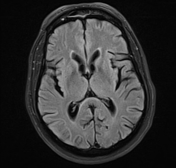



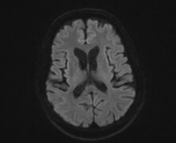

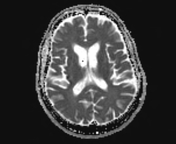

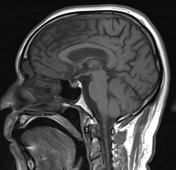

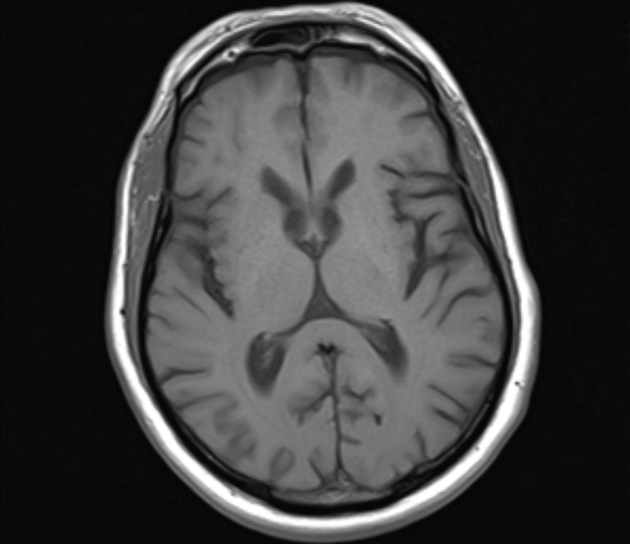
The caudate nuclei are partially atrophied with a mildly widened intercaudate distance. Mild brain atrophic changes are also noted.
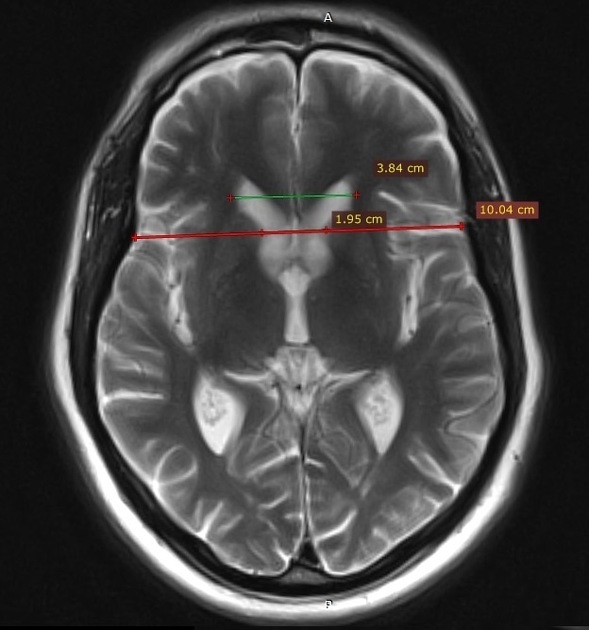
The intercaudate distance to inner table ratio (CC:IT) is increased (0.194; N = 0.09-0.12) and frontal horn width to intercaudate ratio (FH:CC) is decreased (1.96; N = 2.2-2.6).
Measurements have been taken at a slightly oblique angle as to compensate for the effect of head tilt, as to not have false measurements.
Case Discussion
Huntington disease is a neurodegenerative disease that affects the caudate nuclei. It is one of the causes of chorea as well as dementia, behavioral changes, and psychosis. Radiologically, the heads of caudate are atrophied with enlargement of the frontal horns, along with a more generalized cortical atrophy. Measurements that help to assess caudate atrophy include the intercaudate distance to inner table ratio (CC:IT) and the frontal horn width to intercaudate ratio (FH:CC).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.