Presentation
Postmenopausal lady with past history of pulmonary tuberculosis. Presented with fever and shortness of breath. No weight loss, sweating or PV Bleeding.
Patient Data
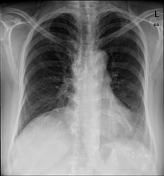
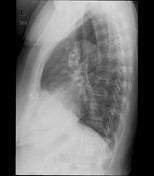
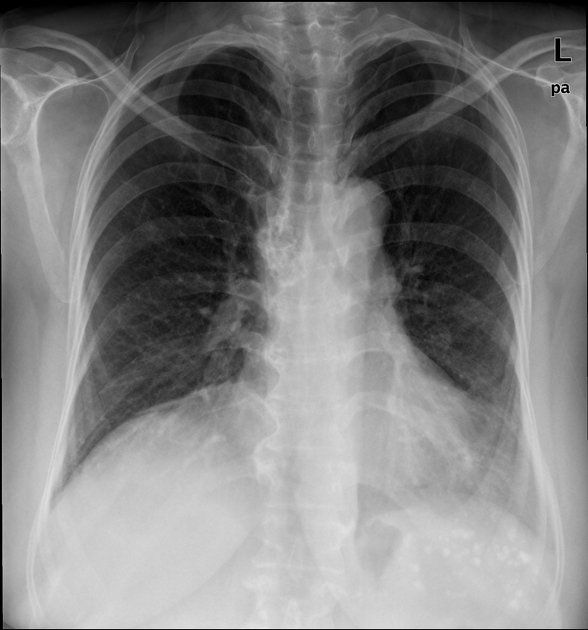
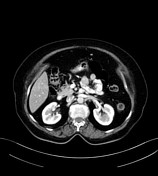
calcified right lower para-tracheal/hilar lymph nodes
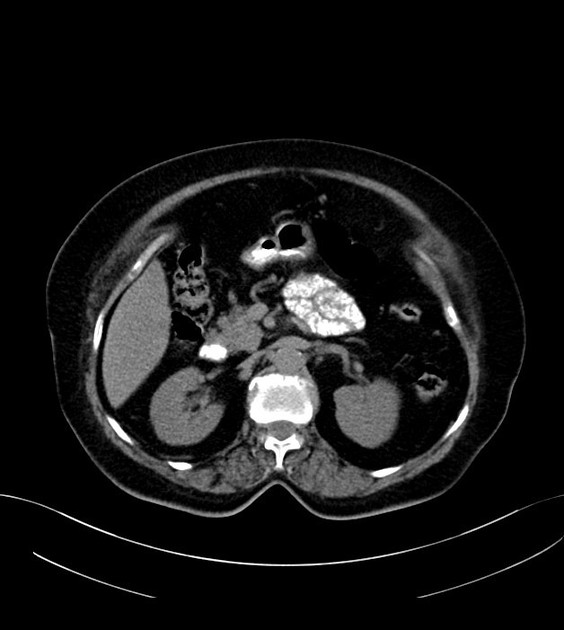
multiple small calcifications in the left hypochondrium which are likely within the spleen (chronic splenic granulomas?)
no consolidation, pleural effusion or pneumothorax is seen
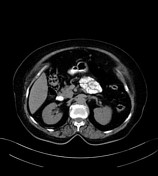


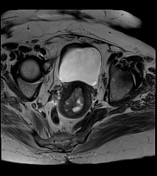
average size retroverted uterus with heterogeneously enhancing endometrial lesion measuring 4.3 x 3.8 x 3.2 cm, without any evidence of myometrial invasion
densely calcified mediastinal (especially right para-tracheal) and multiple abdominopelvic (porta hepatic, aorto-caval, iliac and pelvic) lymph nodes, likely related to the past history of TB
average size spleen with multiple focal calcified lesions and three tiny calcified foci in the peripheral right hepatic lobe (segments 8 and 6); these are likely old granulomas
deformed symphysis pubis, likely related to the previous trauma or infection



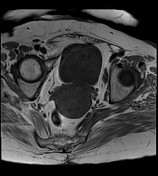

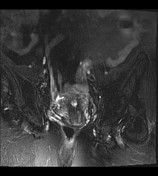

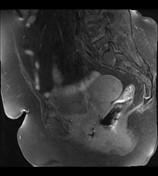

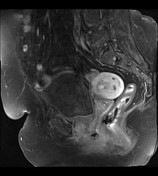

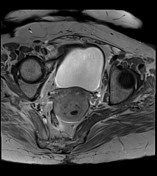

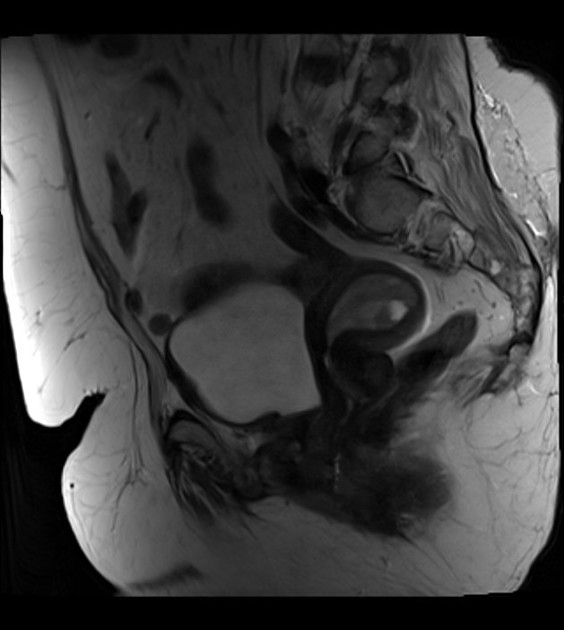
retroverted uterus with heterogeneous endometrial lesion, which shows post-contrast enhancement and has multiple small non-enhancing cystic areas
no evidence of myometrial invasion or suspicious adnexal abnormality seen
Tarlov cyst at S1/S2 level
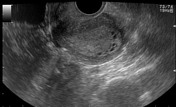
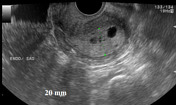
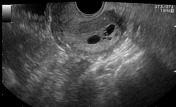
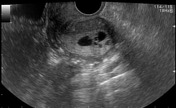
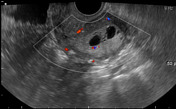
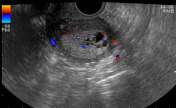
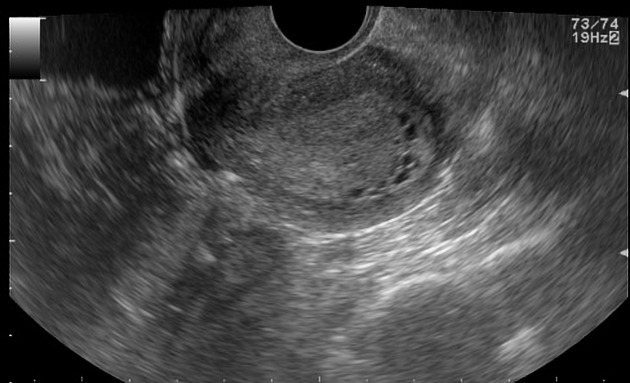
Average size retroverted uterus with diffusely thickened endometrial stripe measuring 20 mm. Multiple small cystic foci are seen within it. Mild vascularity is appreciable in the endometrium on color Doppler ultrasound examination.
Case Discussion
Heterogeneously enhancing endometrial lesion without any evidence of myometrial invasion on CT and MRI and diffusely thickened endometrium with cystic changes on ultrasound in an asymptomatic postmenopausal woman. A few possible causes are endometrial hyperplasia (with cystic changes), endometrial carcinoma, endometrial polyp and submucosal uterine leiomyoma.
Regarding the age of the patient and above described imaging features, the patient underwent diagnostic hysteroscopy, dilatation and curettage. Histopathology showed benign endometrial polyp with focal atypical complex endometrial hyperplasia. Due to these biopsy features, later on the patient underwent total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. Histopathology showed large endometrial polyp, with focal endometrial hyperplasia. No evidence of endometrial malignancy seen. Cervix and ovaries show no significant histological abnormality.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.