Presentation
Known case of bronchogenic cancer under chemotherapeutic treatment.
Patient Data
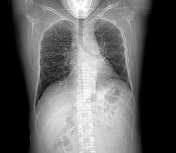

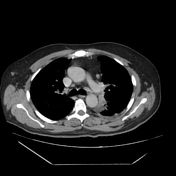



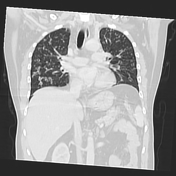

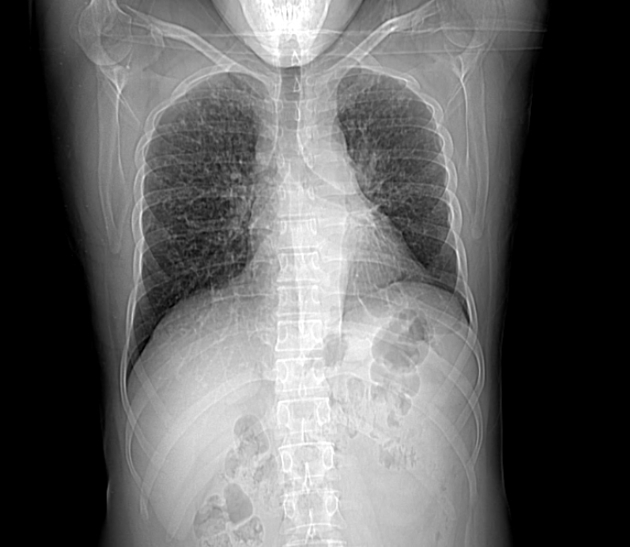
Left upper lobar medial para-aortic irregular shaped soft tissue mass lesion, encasing the descending thoracic aorta and merging with the enlarged left hilar lymph nodes.
Multiple bilateral pulmonary small cavitating nodules.
Mild left pleural effusion.
Multiple mildly enlarged para-tracheal, prevascular, aorto-pulmonary and subcarinal lymph nodes.
Case Discussion
Cavitating pulmonary metastasis occurs most commonly secondary to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung as in this case or the head and neck.
Other primary tumors causing cavitating pulmonary metastasis include:
- gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma
- transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder
- sarcoma
- cervical cancer
Differential diagnosis
- septic pulmonary emboli
- granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- pulmonary TB
- necrobiotic pulmonary nodules




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.