Presentation
Persistent, non-bilious vomiting started after third week of life. The child usually vomits a few minutes after breast feeding.
Patient Data
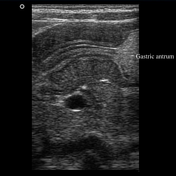
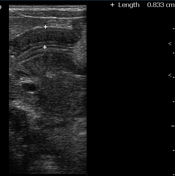
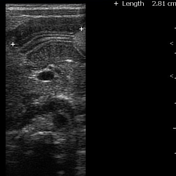
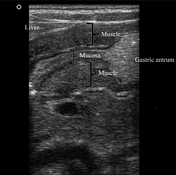
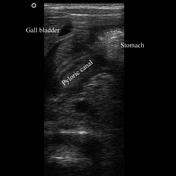
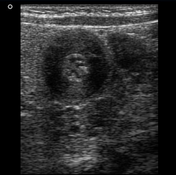
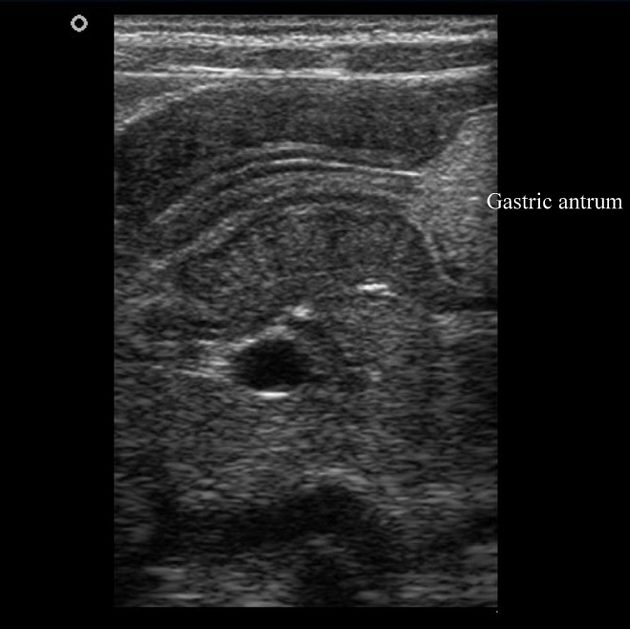
The pylorus is located medial to the gallbladder. Elongated, thickened pyloric canal with a wall thickness of 8.3 mm and a length of 28 mm is observed.
On the transverse images, the hypertrophied pyloric canal gives the appearance of 'target sign'. The Hypertrophied mucosa is seen as hyperechogenic internal layers.
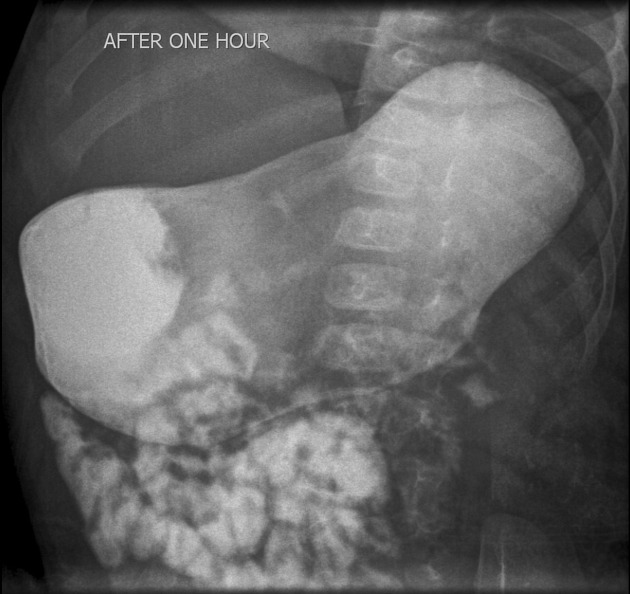
The stomach is distended, a delayed passage of contrast is noted through the pyloric canal. No typical fluoroscopic sign of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis was seen, however, there is evidence of protrusion of the thickened pyloric canal to the gastric antrum.


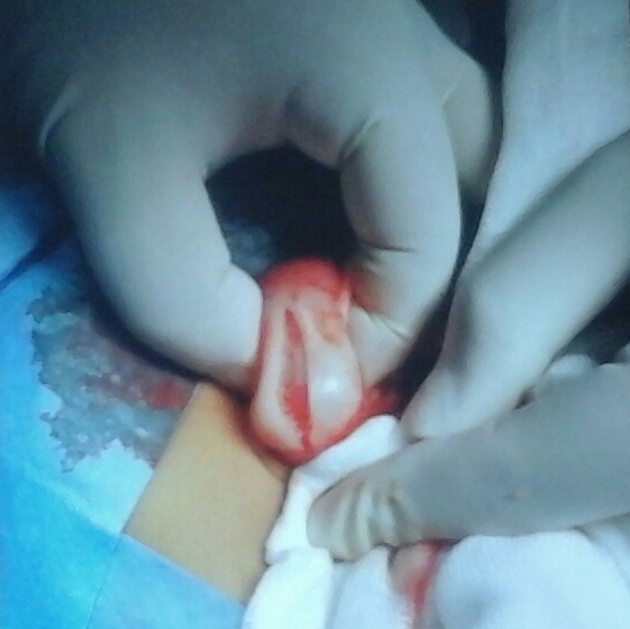
Upper midline incision performed. Typically enlarged and hypertrophied gastric pylorus (Olive sign) was noted. A longitudinal incision of the anterior aspect of the pylorus (pyloromyotomy) was performed until the submucosal layer.
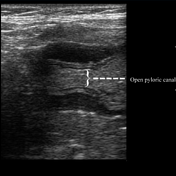
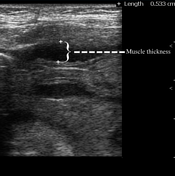
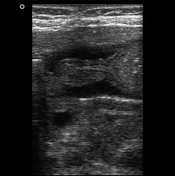
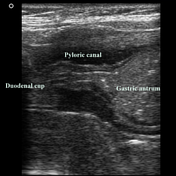
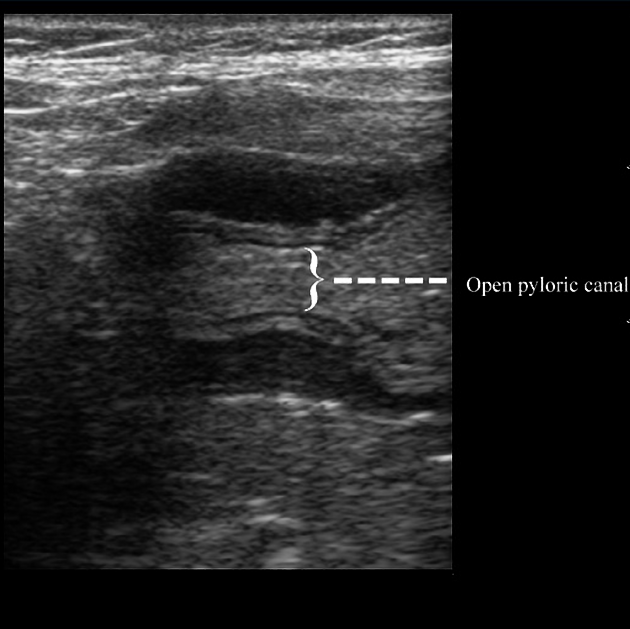
The patient is very well clinically. The child is normally feeding, with No complaint of vomiting. Normal weight gain (the patient weighs 7 Kg).
Ultrasonography reveals a decrease in thickness of the pyloric muscle (5 mm) as well as its length. Real-time images show adequate opening of the pyloric canal and normal passage of gastric content to the duodenum.
Case Discussion
Ultrasonography with the high-frequency linear transducer is the modality of choice for detection of Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS). It allows direct observation of the pyloric canal, usually located slightly medial and posterior to the gallbladder.
The diagnostic criteria for measurement of HPS are the thickness of the muscular layer >3 mm and elongation of the pyloric canal >12 mm.
Upper gastrointestinal series, however, is not the modality of choice for evaluation of HPS, but can exclude other causes of upper gastrointestinal obstruction.
Case contributed by: Dr. Hidayatullah Hamidi, Dr. Jalil Wardak and Dr. Yalda Obaidi.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.