Incidental infundibular pulmonary stenosis and left sided superior vena cava
Presentation
Referral for further evaluation of a pulmonary murmur seen on TTE, for TEE and cardiac MRI. There was no VSD.
Patient Data
- Note: This case has been tagged as "legacy" as it no longer meets image preparation and/or other case publication guidelines.
Is this pulmonic or s...




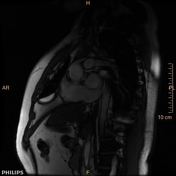

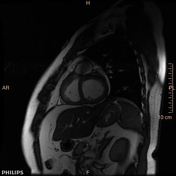

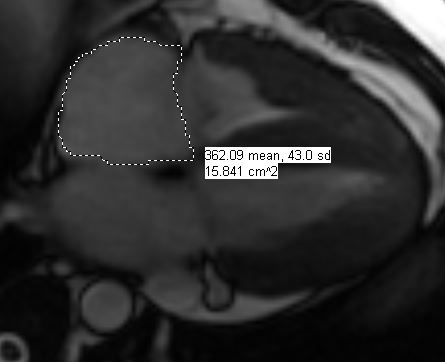
Is this pulmonic or subpulmonic stenosis?
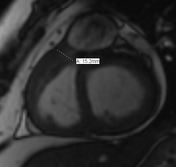
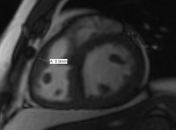
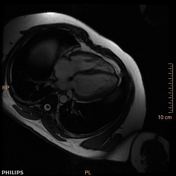
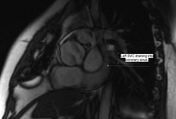
There is severe right ventricular hypertrophy, asymmetric hypertrophy of the RV free wall-RVOT region causing significant subpulmonic stenosis (infundibular pulmonic stenosis). There is no right ventricular dilatation. There is no tricuspid regurgitation. The free wall of the right ventricle measures 9 mm, normally it is less than 4 mm. In the subinfundibular region it is thickened to 15 mm. The right ventricular mass is 70 to 95 grams.
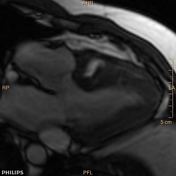
There is dephasing seen across the RVOT from the subpulmonic stenosis. However phase contrast and delayed post contrast was not completed due to patient noncooperation. There is post stenotic dilatation of the main pulmonary artery.
Cardiac MRI series:
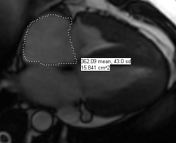
4 chamber SSFP: right atrium measurement.
SAX SSFP: Main PA measurement.
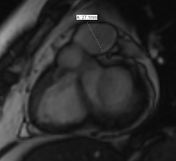
SAX SSFP: Infundibular stenosis measurement.
SAX SSFP: Asymmetric thickness of RVOT.
Axial SSFP: Name the vessel lateral to aortic arch? Trace it down? Where is it terminating? Is there a bridging innominate vein?
4 chamber SSFP: right ventricular hypertrophy.
3 chamber SSFP: Dephasing seen in RVOT from infundibular stenosis.
SAX SSFP: Left SVC.
What is the vessel po...
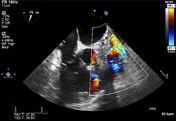
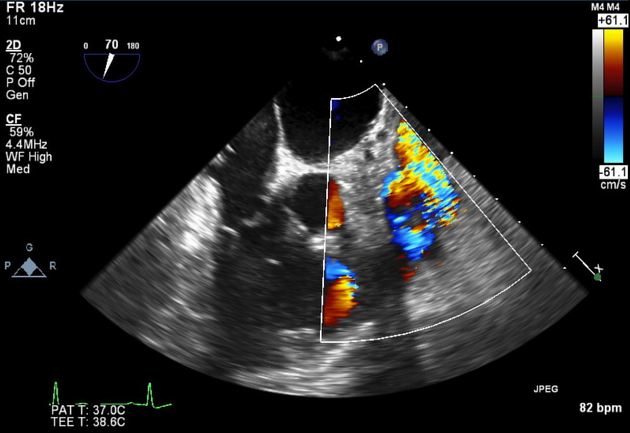
What is the vessel posterior to Lt atrium?
See left SVC draining into coronary sinus and then right atrium.
Recommend cardiac MRI for further definition of RVOT stenosis.
- Left ventricular systolic function is normal.
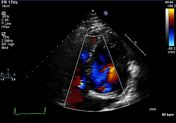
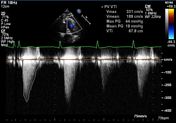
- There is subpulmonic/infundibular pulmonic stenosis. On outside TTE, peak gradient 4.69 m/s. Peak velocity on TEE 3.31 m/s, peak gradient 44 mmHg.
- No VSD identified.
- There is trace aortic regurgitation. There is mild mitral regurgitation. There is mild tricuspid regurgitation.
Case Discussion
Isolated infundibular pulmonic stenosis is an uncommon cardiac abnormality, with a reported incidence of 0.4% of patients with congenital heart disease. There is a duplicated SVC system without a bridging innominate vein draining via the coronary sinus to the right atrium.
Cardiac MRI could confirm the isolated subvalvular infundibular stenosis seen on echo and TEE. Unfortunately patient has been lost to follow up. He needs surgical correction and if not will eventually develop right heart failure.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.