Acromial apohysiolysis is a finding on shoulder MRI that may be encountered in patients with an unfused acromial apophysis. It is associated with athletes in throwing sports.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Presents with superior shoulder tenderness in a patient <25 years old, often in a young throwing athlete (~100 pitches/week in American baseball). May clinically mimic a shoulder labral tear.
Pathology
Repetitive stress across a meta-acromion-meso-acromion type unfused acromion. The injury is analogous to epiphysiolysis at incompletely fused growth plates.
Radiographic features
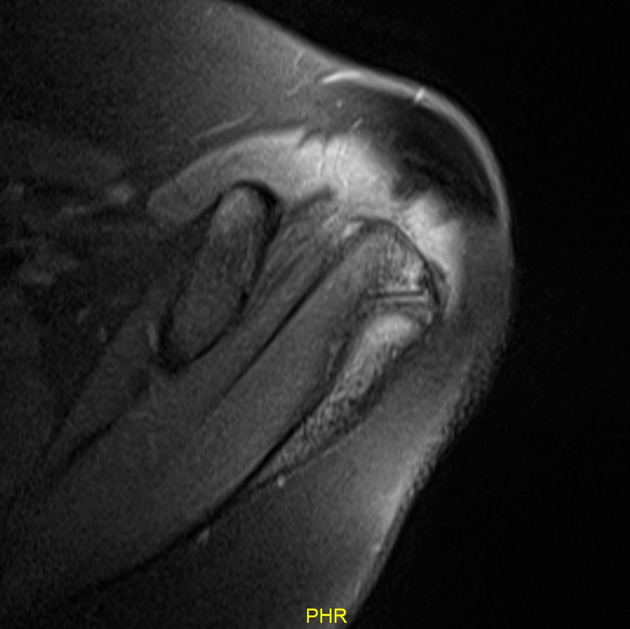
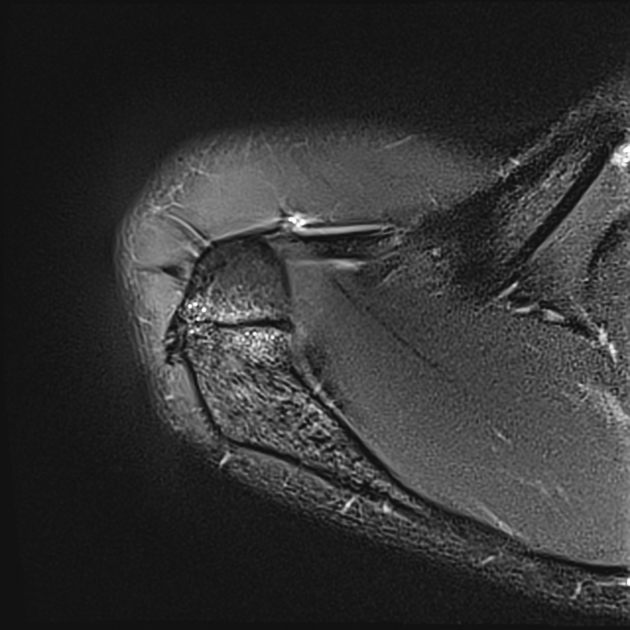
MRI
-
STIR / PD FS
increased signal intensity across an unfused acromion
STIR sequence is useful to avoid inhomogeneous fat suppression
-
T1
decreased signal intensity across an unfused acromion
Treatment and prognosis
Patients are usually treated conservatively, with rest and NSAIDs.
It is associated with an eventual os acromiale formation (86% vs. 4% control) and rotator cuff tear (after age >25 years) if the cause of the shoulder stress is not discontinued.
Practical points
in a throwing athlete with shoulder pain, edema signal intensity across an unfused acromial apophysis, and no other cause for shoulder pain consider acromial apophysiolysis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.