This is a basic article for medical students and other non-radiologists
Air-space opacification is a descriptive term that refers to filling of the lung parenchyma with material that attenuates x-rays more than the unaffected surrounding lung tissue. It is the radiological correlate of the pathological diagnosis of pulmonary consolidation.
On this page:
Reference article
This is a summary article; read more in our article on air-space opacification.
Summary
-
anatomy
-
pathophysiology
-
material fills the lung parenchyma
fluid: pulmonary edema
pus: pneumonia
blood: pulmonary hemorrhage
cells: malignancy
protein: alveolar proteinosis (rare)
-
distribution
-
patchy
air-space filling is incomplete and non-contiguous
residual gas within the alveoli
-
lobar
complete filling of a lobe of the lung
-
clear delineation between consolidation and adjacent gas-filled structures
the remainder of the lung or in bronchi traveling through the lobe
-
no margin between consolidation and other soft-tissue density structures
mediastinum or diaphragm
-
multifocal
symmetrical or asymmetrical
perihilar or peripheral
often non-specific without clinical history and examination findings
-
-
-
role of imaging
confirm air-space opacification and differentiate from atelectasis or pleural effusion where possible
help to determine the cause, e.g. other signs of heart failure
identify complications, e.g. abscess formation
demonstrate accompanying pathology, e.g. effusion or empyema
determine severity and extent, e.g. number of lobes involved, uni- or bilaterality
-
common pathology
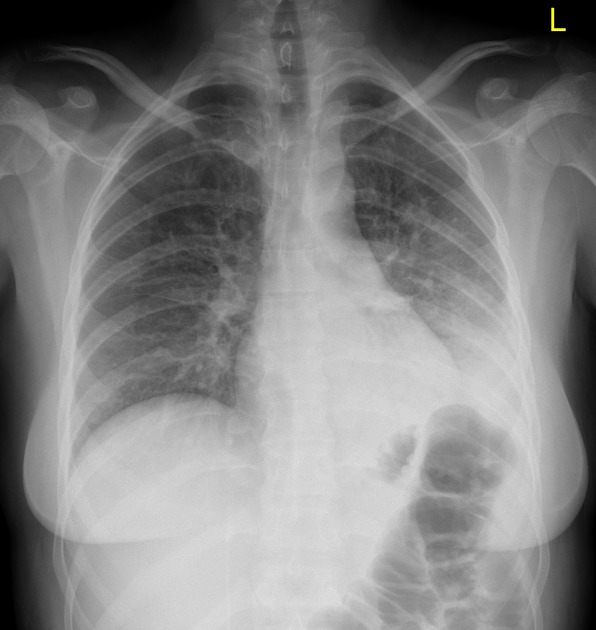
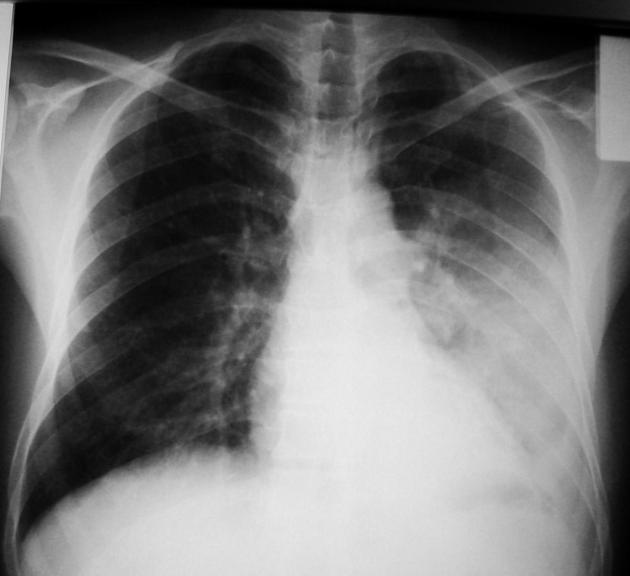
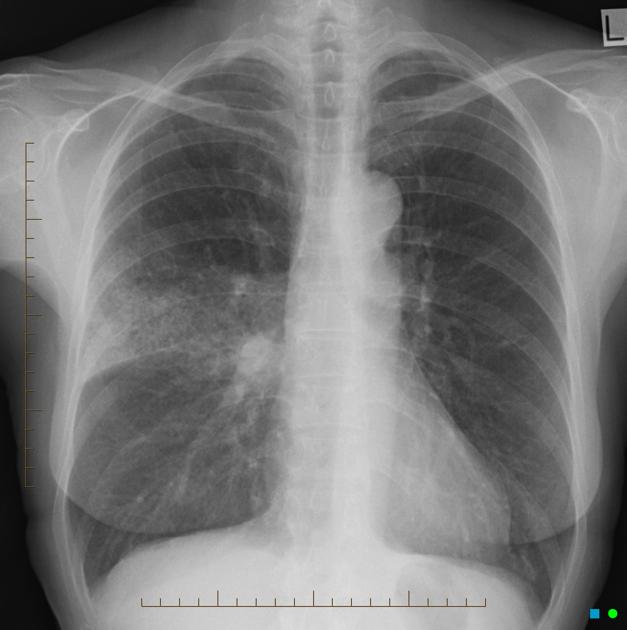
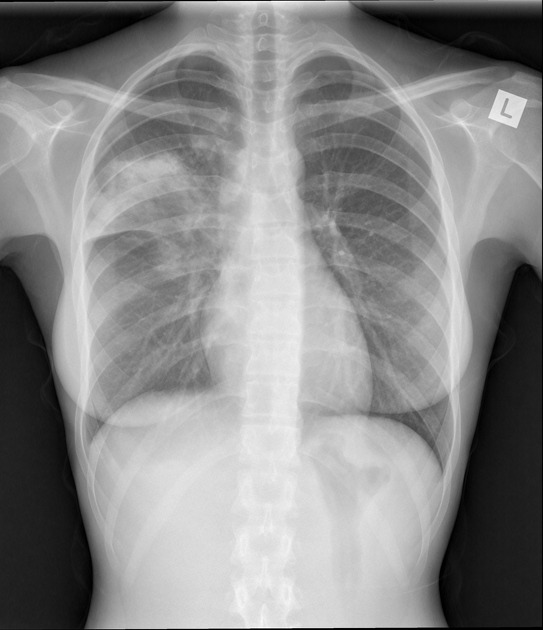
Radiographic features
Chest x-ray
normal air-filled lung is black
air-space opacification is radiopaque (white)
aerated bronchi
CT chest
-
air-space opacification looks very similar to the chest x-ray
distribution can be assessed more accurately
assessment of complications is more accurate





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.